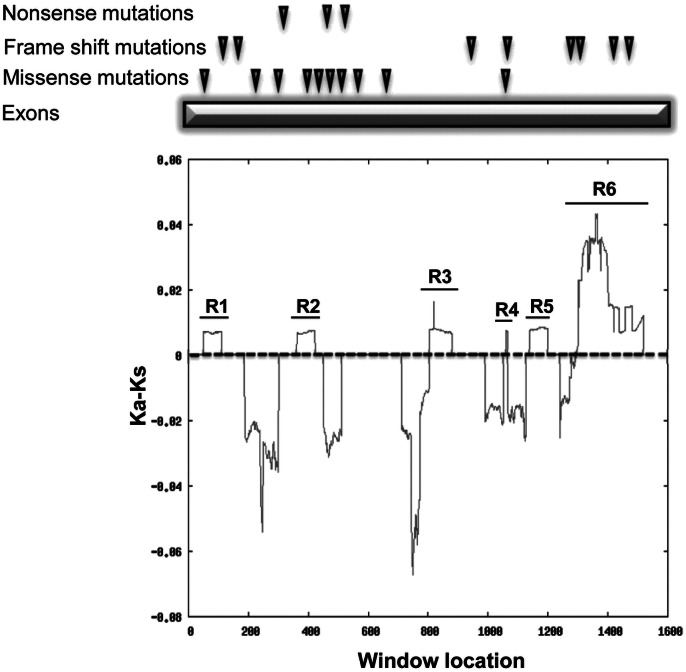
Fig. 3.
Sliding window analysis of WDR62.
Human and chimpanzee coding sequences were subjected for this analysis. Peaks (R1–R6) above the threshold (Ka − Ks = 0, dotted line) indicate the excess of non-synonymous substitution over neutral expectation, i.e. Ka − Ks > 0. Previously reported mutations in WDR62 that cause microcephaly are depicted on top of the plot.