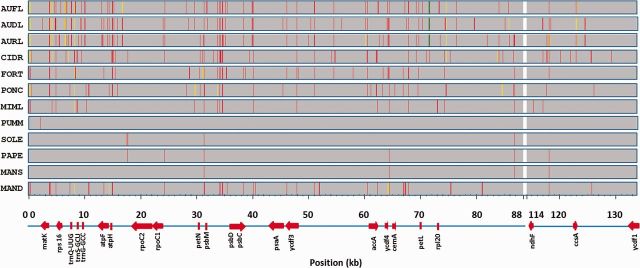
Fig. 2.
Distribution of indels along the chloroplast citrus genomes in 100-bp nonoverlapping windows. MAND, mandarins (Clementine, Willowleaf, Ponkan, Satsuma, Dancy, King, W Murcott, Huanglingmiao, Cleopatra, Sunki, and Rangpur lime); MANS, Mangshan mandarin; PAPE, Ichang papeda; SOLE, Sour orange and Eureka lemon; PUMM, pummelos and grapefruits (Chandler, low-acid, Guanxi, Shatian, and Marsh); MIML, Micrantha and Mexcian lime; PONC, Pomeroy; FORT, Calamondin and kumquat; CIDR, citrons (Buddah’s Hand, Mac Veu Montain, Humpang, and Corsican); AURL, Australian round lime; AUDL, Australian desert lime; and AUFL, Australian finger lime. The Citrus sinensis chloroplast genome was used as the reference genome and the two inverted repeats IRa (133–160 kb) and IRb (88–114 kb) of this genome were not included in the study. Colors represent number of indels: red: 1; yellow: 2; and green: 3. Positions of genes cited in the text are depicted as reference.