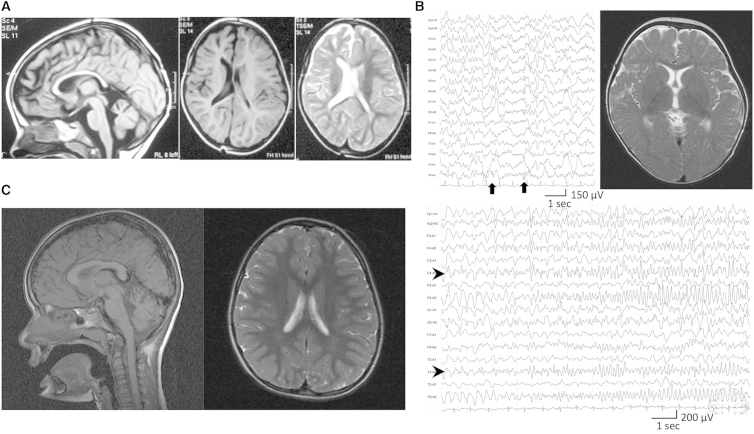
Figure 2.
MRI and EEG of the Affected Individuals
(A) MRI of individual EG02 when she was 2.5 years old. (Left panel) Mid-sagittal T1-weighted MRI shows the thin corpus callosum. (Right panel) Axial plane in T1- and T2-weighted MRI shows asymmetry of the lateral ventricles.
(B) MRI and EEG of individual JP01. (Upper left panel) Interictal EEG during sleep at the age of 3 years shows focal spikes on the right posterior area (C4-P4-O2-T6, arrows). (Lower panel) Ictal EEG at 14 months shows that low-amplitude fast waves arose from right centrotemporal lesions (C4-T4, arrowheads) and then propagated to the entire right hemisphere. According to the ictal discharge, the individual developed eye deviation and head turning to the right after clonic seizures of the left upper extremity. (Upper right panel) T2-weighted brain MRI at the level of basal ganglia shows normal appearance at 11 months.
(C) MRI of individual PK01. (Left panel) Mid-sagittal T1-weighted MRI shows cerebellar hypoplasia. (Right panel) Axial plane in T2-weighted MRI shows mild cerebral atrophy.