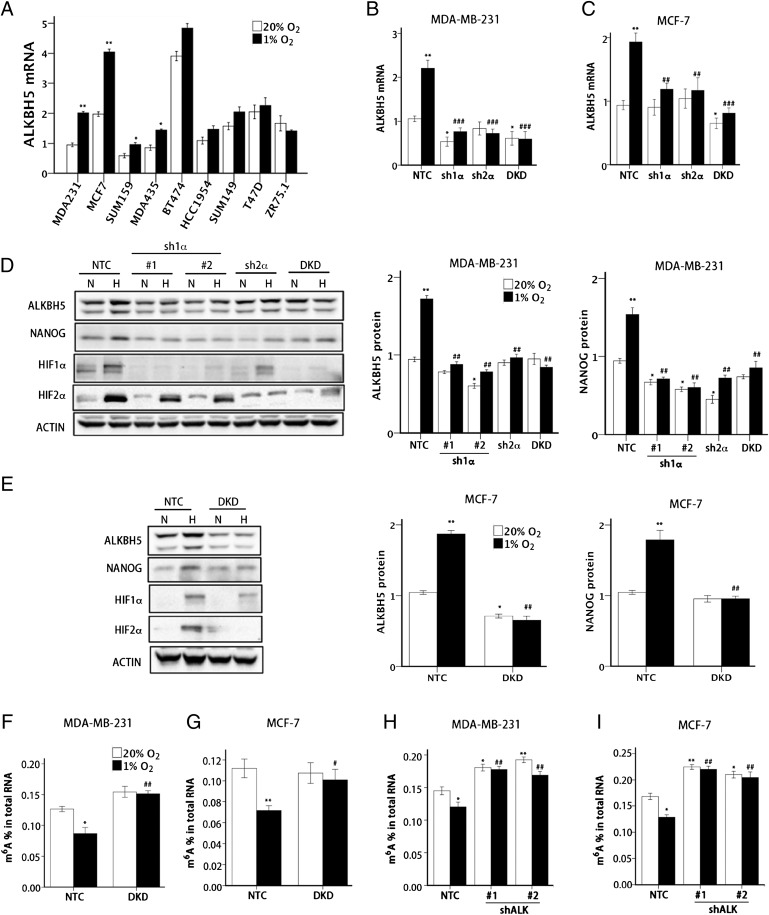
Fig. 1.
Hypoxia-induced and HIF-dependent ALKBH5 expression mediates a reduction in total RNA m6A levels. (A) Nine human breast cancer cell lines were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 24 h, and ALKBH5 mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR relative to 18S rRNA and normalized to the mean value for MDA-MB-231 cells (MDA231) at 20% O2 (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. same cell line at 20% O2). (B and C) NTC, sh1α, sh2α, and DKD subclones of MDA-MB-231 (B) and MCF-7 (C) were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 24 h, and RT-qPCR was performed to determine ALKBH5 mRNA levels relative to 18S rRNA. The results were normalized to NTC at 20% O2 (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 20% O2; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 vs. NTC at 1% O2). (D and E) MDA-MB-231 (D) and MCF-7 (E) subclones were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 48 h, whole cell lysates were prepared, and immunoblot assays were performed to analyze HIF-1α, HIF-2α, ALKBH5, and NANOG protein expression. Actin was also analyzed as a loading control. The intensity of ALKBH5 and NANOG bands were determined, and the data were normalized to NTC at 20% O2 (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 20% O2; ##P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 1% O2). (F and G) MDA-MB-231 (F) and MCF-7 (G) NTC and DKD subclones were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted and m6A levels were determined as a percentage of all adenosine residues in RNA (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 20%; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 1% O2). (H and I) MDA-MB-231 (H) and MCF-7 (I) NTC and ALKBH5 knockdown (i.e., shALK) subclones were exposed to 20% or 1% O2 for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted, and m6A content was determined as a percentage of all adenosine residues (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 20% O2; ##P < 0.01 vs. NTC at 1% O2).