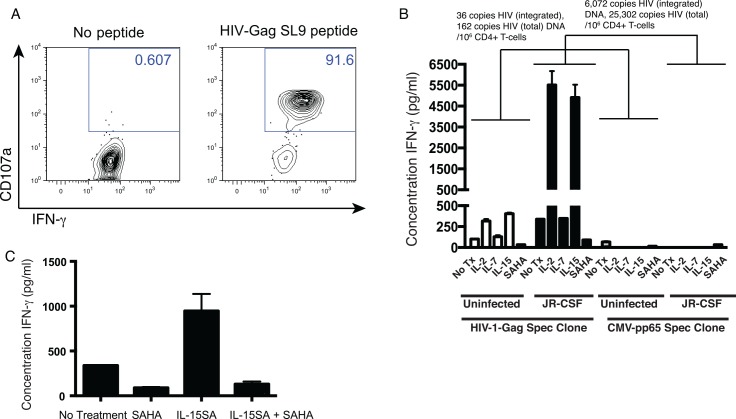
Fig 3. A subset of latency-reversing agents prime latently-infected CD4+ T-cells for CD8+ T-cell recognition in a continuous co-culture assay.
A. An HIV-Gag-SLYNTVATL (SL9) specific CD8+ T-cell clone was isolated from subject OM9. To confirm specificity, this clone was co-cultured with an autologous B lymphoblastoid cell line (BLCL) that had been pulsed with 1 μg/ml of SL9 peptide or with an unpulsed control. Shown are flow cytometry data gated on CD8+ lymphocytes, depicting CD107a staining (degranulation)–y-axis by IFN-γ –x-axis. These data indicate that the CD8+ T-cell clone to be used in subsequent panels was highly specific. B. CD4+ T-cells latently infected with HIV-JR-CSF, or mock infected, as described in Fig 1, using leukapheresis material autologous to the CD8+ T-cell clone in A. Total and integrated HIV DNA were quantified by qPCR. These cells were treated with the indicated drugs at the following concentrations: IL-2 1.3 nM, IL-7 1 nM, IL-15 1.4 nM or SAHA 500 nM for 72 hours in the presence of nevirapine. These concentrations of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 equate to 20 ng/ml, and were selected based on concentrations used in previous studies of latency reversal [32,33]. Target cells were then co-cultured with the HIV-Gag-specific CD8+ T-cell clone from A for an additional 72 hours. Shown are IFN-γ levels quantified in supernatants (mean ± SEM). These results indicate that IL-2 and IL-15 primed latently-infected cells for recognition by CD8+ T-cells. C. An experiment was setup in an identical manner to B, co-culturing with an HIV-Gag-SL9-specific CD8+ T-cell clone in the presence of the indicated single of combinations of drugs at the following concentrations: SAHA 500 nM; IL-15SA 1.4 nM. Shown are mean ± IFN-γ quantifications (ELISA).