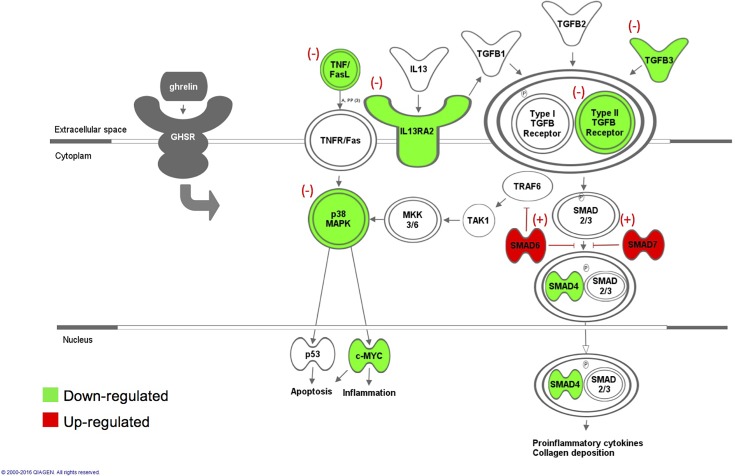
Fig 6. Ghrelin-induced anti-inflammatory effect is mediated by inhibition of TGF-β/Smads and p38-MAPK signaling pathways.
A representative diagram characterizing the possible pathways by which ghrelin modulates the inflammatory response. Ghrelin binding to the GHSR receptor negatively modulates TGF-βR2, TGF-β3, TNF and IL13RA2 and up-regulates the inhibitory proteins SMAD7 and SMAD6, establishing the inhibition of TGF-β/Smads and p38-MAPK signaling pathways. This diagram was designed loading the fold change of ghrelin-treated samples versus controls into the Ingenuity pathway analysis software. Red highlighted genes represent overexpression and green represents underexpression of the factors of these pathways after ghrelin administration.