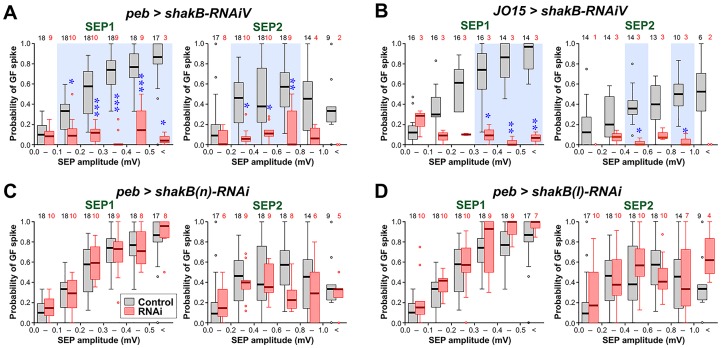
Fig 5. ShakB knockdown with different RNAi lines and drivers.
Box-whisker plots of the probability of GF spiking in response to SEP1 and SEP2. Controls are shown in gray, experimental data in pink. Statistically significant differences between RNAi versus control (Mann-Whitney test, Bonferroni p-correction for 6 comparisons) are indicated with blue asterisks and a light blue background tint. (A) The Vienna GD12666 line (shakB-RNAiV) strongly decreases the GF response to both SEPs. (B) The same line, driven by JO15-GAL4 (without Dcr-2) in auditory JONs alone, is also effective at inhibiting the GF response. (C) The JF02603 line, which targets shakB(n) (shakB(n)-RNAi) has no effect on the JON-GF connection. (D) The JF02604 line, which targets shakB(l) (shakB(l)-RNAi) also has no effect on the JON-GF connection. For full genotypes see S1 Table.