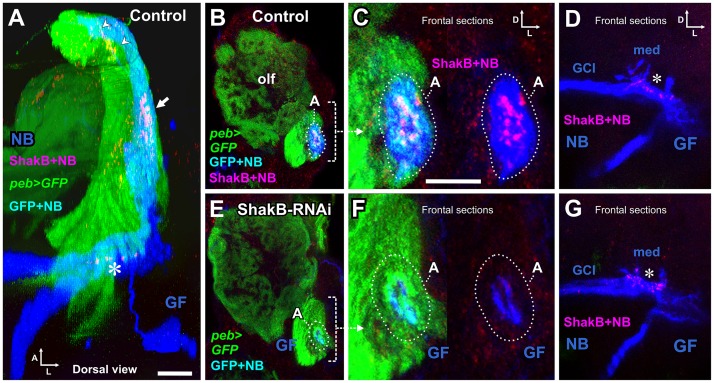
Fig 8. ShakB immunostaining and RNAi knockdown.
(A) Dorsal view of a complete confocal stack of a control animal, in which peb-GAL4 drives expression of CD8::GFP (green) and Dcr-2 in JON axons (and other sensory neurons—for clarity, olfactory axons are shown as partially transparent). Neurobiotin (NB: blue) is injected into the GF and transfers across gap junctions into the green JO-A axons (to appear cyan). The red channel shows immunostaining for the gap junctional protein ShakB, which forms plaques in the JON-A axons (arrow) and on the medial GF dendrite (asterisk). Scattered staining is also present in the antennal nerve (arrowheads). (B) Maximum intensity projection of 3 frontal slices, showing peb-driven GFP staining in olfactory glomeruli (olf) and JON axons. The A group of the latter is indicated (dotted oval), showing NB dye transfer (cyan). (C) High power view of the A axons, showing the ShakB plaques overlying the NB staining (magenta), which are seen more clearly in the right panel where the green channel is omitted. (D) Projection of 20 frontal sections through the GF medial dendrites (med) and coupled giant commissural neurons (GCI). ShakB plaques (magenta) are present on the medial GF dendrite (asterisk). (E-G) Experimental animal in which peb-GAL4 drives expression of CD8::GFP, Dcr-2 and shakB RNAi. (E, F) ShakB staining is not present around the NB-filled GF dendrites, nor does NB pass into the A axons (dotted oval). (G) ShakB staining on the GF medial dendrite is unaffected by RNAi in the JONs. For full genotypes see S1 Table. Scale bar in A: 20 μm in A, B, D, E, G; Scale bar in C: 10 μm in C and F.