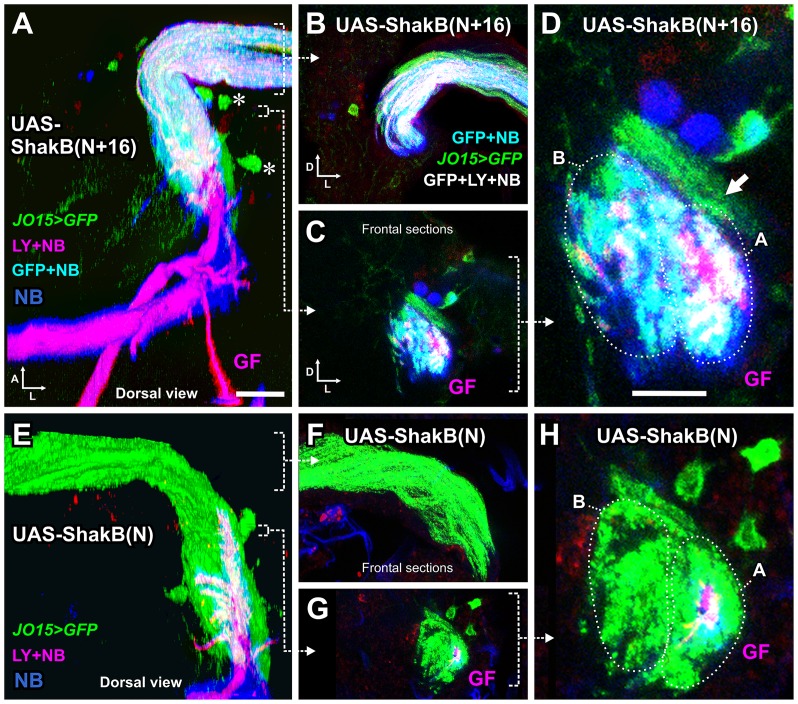
Fig 9. Expression of different isoforms of ShakB in JON axons alters dye coupling to the GF.
(A-D), JO15-GAL4 drives expression of UAS-ShakB(N+16) in JO-A and JO-B neurons, along with CD8::GFP to label the axons. LY and NB are injected into the GF and NB is transferred across gap junctions into the JON axons. Some LY also appears to be transferred. (A) is a dorsal view of a 3D reconstruction, (B-D) are Z projections of frontal slices. (B) is a projection of several slices through the nerve, in order to show the NB and LY within the axons. (C) and (D) are low and high power views of slices through the axons in the region of the GF dendrite. (D) The A and B groups of axons are indicated (dotted ovals), along with another group of peripheral A axons that do not dye couple (arrow). (E-H) JO15-GAL4 drives expression of the ShakB(N) isoform and abolishes gap junctional coupling. (F) Projection of sections through the nerve, showing the absence of coupling (compare with B). (H). High power frontal section through the axons in the region of the GF dendrite, showing only the GF filled with both NB and LY. For full genotypes see S1 Table. Scale bar in A: 20 μm in A, B, C, E, F, G; Scale bar in D: 10 μm in D and H.