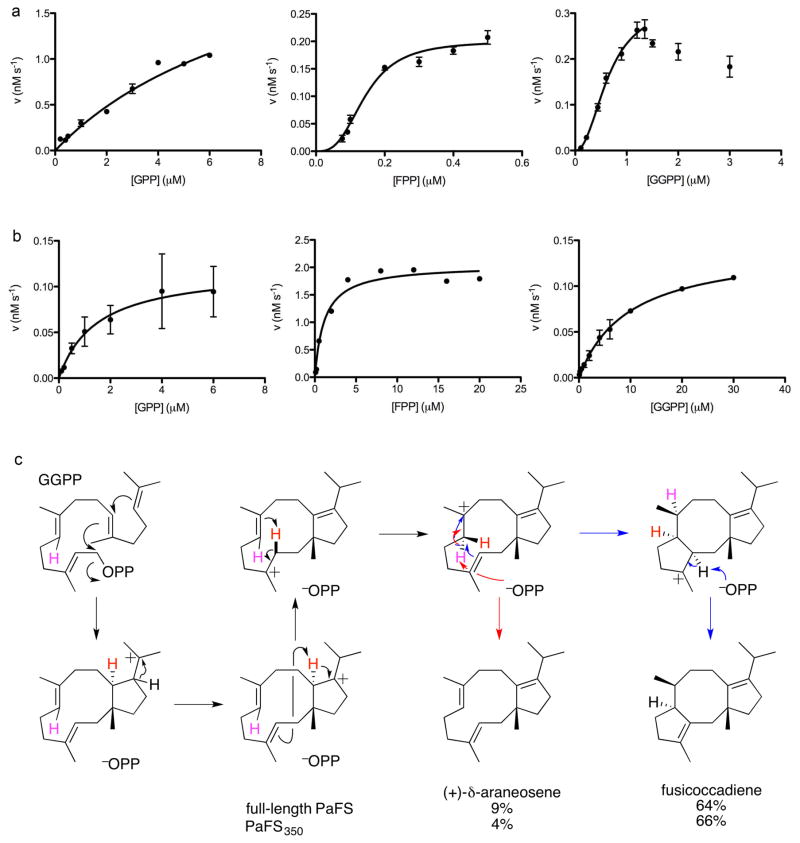
Figure 2. Catalytic activity measurements.
(a) Generation of hydrocarbon products from substrates GPP, FPP, and GGPP in the absence of IPP (the concentrations of full-length PaFS in these experiments were 74.5 nM, 7.45 nM, and 14.9 nM, respectively). Catalysis with GPP exhibits Michaelis-Menten kinetics, whereas catalysis with FPP or GGPP exhibits cooperativity based on the sigmoidal dependence of catalytic activity on substrate concentration. With GGPP, substrate inhibition is evident at higher concentrations. (b) PaFS350 (33.5 nM) exhibits Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the generation of hydrocarbon products from substrates GPP, FPP, and GGPP. (c) Proposed cyclization mechanism29 for the generation of fusicoccadiene (black and blue arrows) and δ-araneosene (black and red arrows) by full-length PaFS and PaFS350 (a third, unidentified diterpene product is also generated).