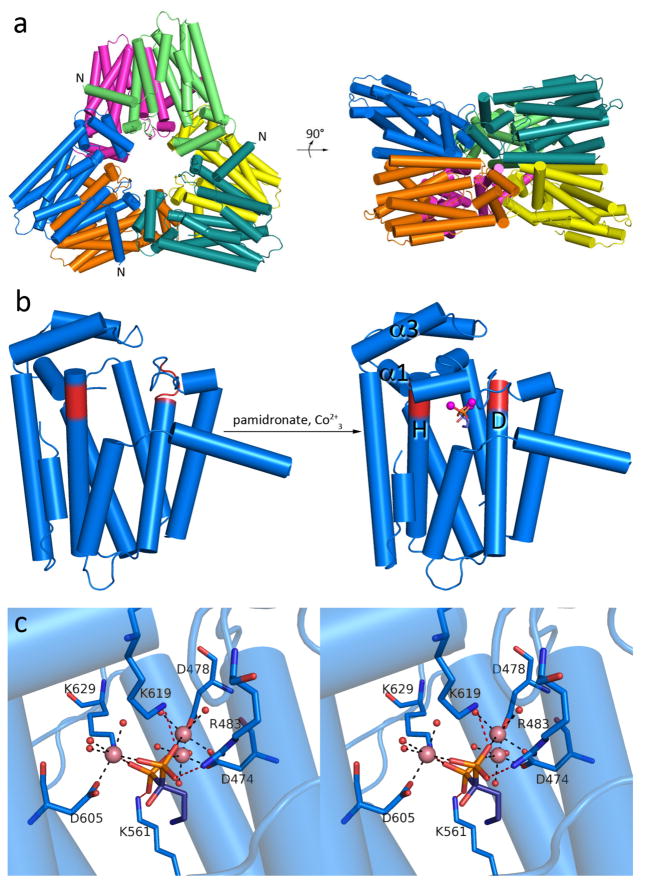
Figure 3. PaFS C-terminal GGPP synthase domain.
a) PaFSCT adopts the α fold of a class I terpenoid synthase and crystallizes as a hexamer, or a trimer of dimers. The N-termini of selected subunits are labeled and indicate the point of connection to the missing N-terminal domain. Two perpendicular orientations are shown. (b) The binding of 3 Co2+ ions and pamidronate triggers complete closure of the active site of PaFSCT. (c) Stereoview of intermolecular interactions in the PaFSCT-Co2+3-pamidronate complex. Metal coordination and hydrogen bond interactions are shown as black and red dashed lines, respectively (metal-ligand distances are recorded in Supplementary Information Table S3). Pamidronate binds in the DMAPP binding site, so interactions of the phosphonate groups mimic interactions with the diphosphate group of DMAPP that trigger ionization and formation of the allylic cation that initiates the chain elongation reaction.