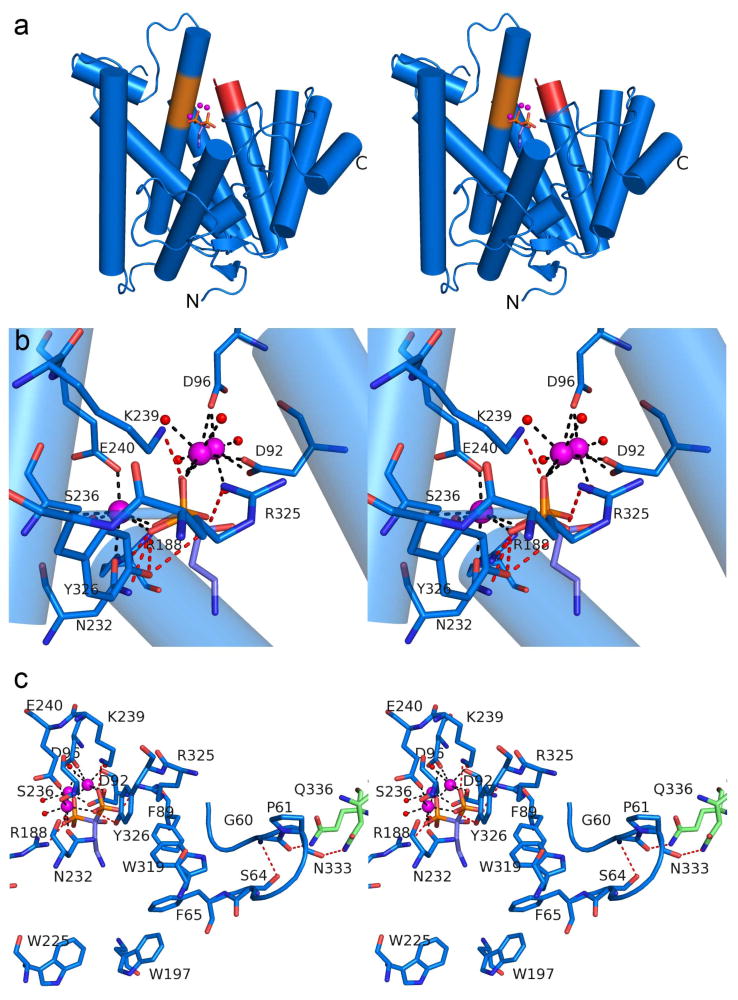
Figure 4. PaFS N-terminal GGPP cyclase domain.
(a) Stereoview of the PaFS344-Mg2+3-pamidronate complex reveals that the N-terminal domain adopts the α fold of a class I terpenoid synthase. (b) Stereoview of the PaFS344-Mg2+3-pamidronate complex showing metal coordination and hydrogen bond interactions as black and red dashed lines, respectively (metal-ligand distances are recorded in Supplementary Information Table S3). (c) The G60-F65 hairpin segment may facilitate communication between cyclization domain active sites in full-length hexameric PaFS by mediating interactions between active site residue F65 and interdomain linker residues N333 and Q336 (green).