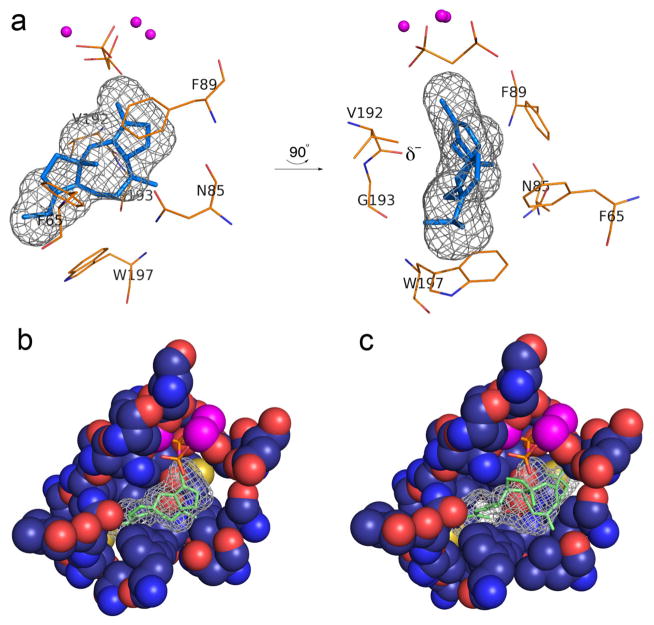
Figure 5. Models of enzyme-product complexes.
(a) Model of product fusicoccadiene bound in the active site of PaFS344. The three-dimensional active site contour is represented by black meshwork, and fusicoccadiene was manually fit into this meshwork. The position of the Mg2+3-PPi cluster is modeled after the Mg2+3-bisphosphonate cluster in the PaFS344-Mg2+3-pamidronate complex. Two perpendicular views are shown; the backbone carbonyl of V192 at the helix G break (δ−) is oriented toward the location of a proposed carbocation intermediate in the PaFS mechanism. (b) Cut-away view of the active site pocket of PaFS344, showing how the surface contour (black meshwork) is defined by residues lining the pocket. (c) Ophiobolin F docked in the active site of ophiobolin F synthase modeled after the PaFS344-fusicoccadiene complex in (b). The extra active site volume resulting from the W225L and V228A substitutions readily accommodate the larger C25 sesterterpene.