Fig. 6. Subretinal injection of AAV expressing Txnip shRNAs inhibits cone OS synthesis and electrophysiology and induces constitutive activation of Akt in cones, but it does not affect rod OS formation or rod electrophysiology.
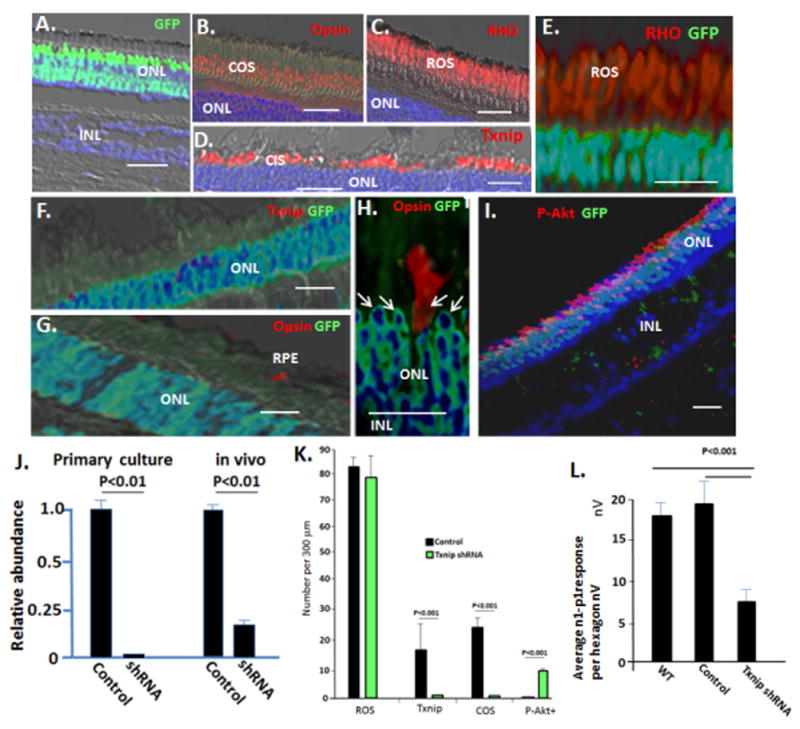
AAV viruses (Fig. S6) were injected in 30 μl subretinally into the region of the visual streak in WT pigs at P60, as described for cells and glucose in Figs. 3–5. Eyes were harvested after 4 weeks. (A–D) Control AAV expressing GFP and a scrambled Txnip shRNA sequence (Fig. S6) infects photoreceptors, but does not affect expression of Txnip or formation of cone or rod OS. (E) AAV expressing Txnip shRNA and GFP does not affect RHO+ rod OS formation or electrophysiology (Fig. S6). (F) Txnip shRNA AAV inhibits Txnip expression. (G–H) AAV expressing Txnip shRNA inhibits cone opsin+ OS formation. Note opsin+ cone OS are confined to uninfected GFP− cells. Arrows indicate cone nuclei, which are confined to the outer two rows of the ONL, where rods are excluded (Fig. 2A). (I) AAV expressing Txnip shRNA causes activation of Akt (P-Akt) in cones, which as noted, comprise the outer two ONL rows in the pig. Note infected rods, which make up the inner rows of the ONL, do not activate Akt. GFP is not expressed from the viral EF1a promoter following infection of RPE or Muller cells (Fig. S6). (J) Real time PCR analyzing expression of Txnip mRNA in WT neural retina following infection with AAV Txnip shRNA in vivo (as in panels A–I, see Fig. S6 for viral GFP expression in the optic cup and sites of RNA isolation), and in vitro in primary culture of WT neural retina at P14. (K) Quantification of results in panels A–I. (L) Quantification of the effects of AAV on photopic mfERG. See Fig. S6 for representative mfERG and ffERGs. Control virus n=5; Txnip shRNA viruses n=8. Bars are 30 μm. Standard deviations are shown.
