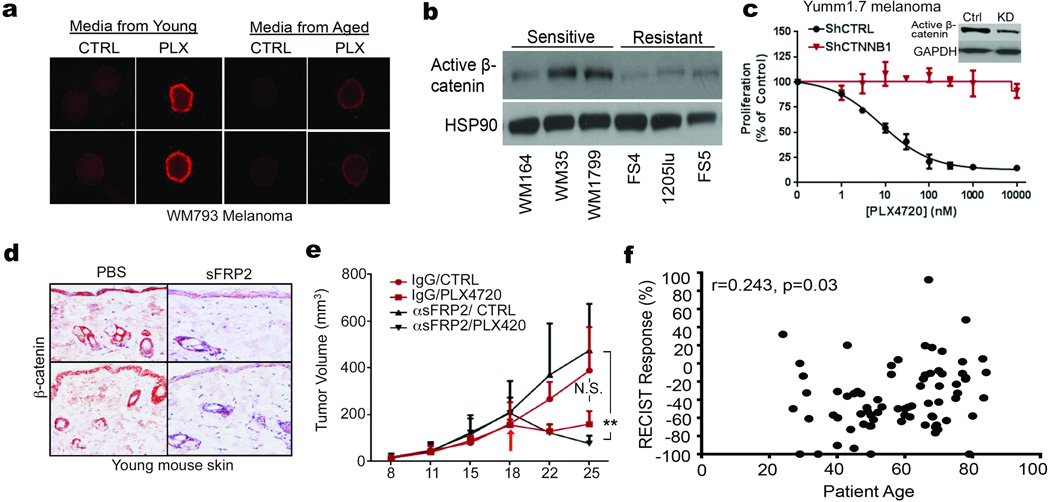
Extended Data 9. β-catenin predicts for sensitivity to vemurafenib.
Melanoma spheroids were embedded in collagen and treated with 1µM PLX4720 in the presence of conditioned media from either young or aged fibroblasts. After 48h, spheroids were assessed for cell death by staining with ethidium homodimer (magnification, 40×) (a). In cells intrinsically sensitive to vemurafenib in culture, β-catenin expression is increased (b). Knockdown of β-catenin in Yumm1.7 cells decreases their sensitivity to PLX4720. Spearman’s correlation between dose and percent proliferation is significant in CTRL cells [p<0.0001, r=−1.000] whereas shCTNNB1 cells indicated no significant changes in curve after treatment [p=0.948, r=0.03] (c). Young mice (8 weeks, n=10 /group) were injected with rsFRP2 (200ng/mL, twice weekly) and skin was examined for β-catenin levels by immunohistochemistry. Representative images, magnification 200× (d). Yumm1.7 tumors were injected in aged mice pre-treated with α-sFRP2 antibody (1mg/kg, once weekly). Mice were then administered either control or 417mg/kg PLX4720 laced chow. Analysis of variance is significant between treatments (p<0.0001). Two-tailed unpaired t test using rank sum (Mann Whitney) was performed on tumor volumes on day 25 (1 week after treatment). Results were significant in sFRP2 treatment (p=0.036) and insignificant in IgG2aκ treatment (p=0.057) (e). Patient samples show a continuum of decreased response in relation to age, Spearman’s correlation between percent response and age is significant [r=0.243, p=0.035] (f). Data are represented as mean ± s.d for each graph (c,e).