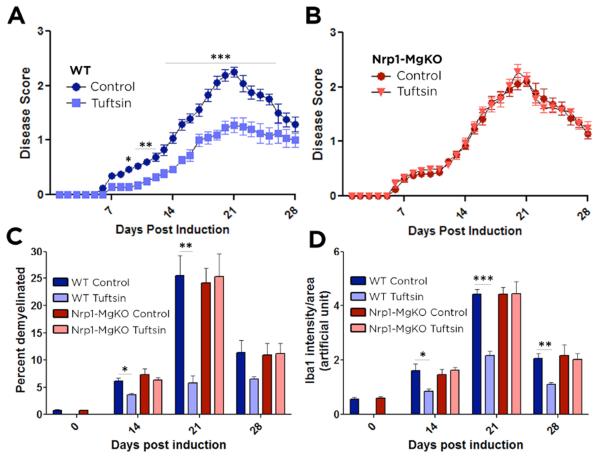
Figure 1. Tuftsin infusion has no effect on EAE disease symptoms in Nrp1-MgKO mice.
EAE was induced by injection of MOG35-55 in CFA and pertussis toxin. Osmotic pumps filled with 500μM tuftsin in PBS were implanted subcutaneously on day 0 after MOG immunization. Comparisons between WT control (untreated) and tuftsin-infused mice (A) and Nrp1-MgKO control (untreated) and tuftsin-infused mice (B). Data are mean ± SEM. n= 13-17, *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001. (C) Frozen spinal cord sections were isolated from control and tuftsin-infused WT and KO mice at 0, 14, 21, and 28 days post induction of EAE. Demyelination was quantified by fluoromyelin staining and demyelinated areas were measured using ImageJ and quantified. (D) Quantification of Iba1 signal intensity staining was utilized to detect microglia in control and tuftsin-infused WT and Nrp-MgKO mice at 0, 14, 21, and 28 days post induction of EAE.