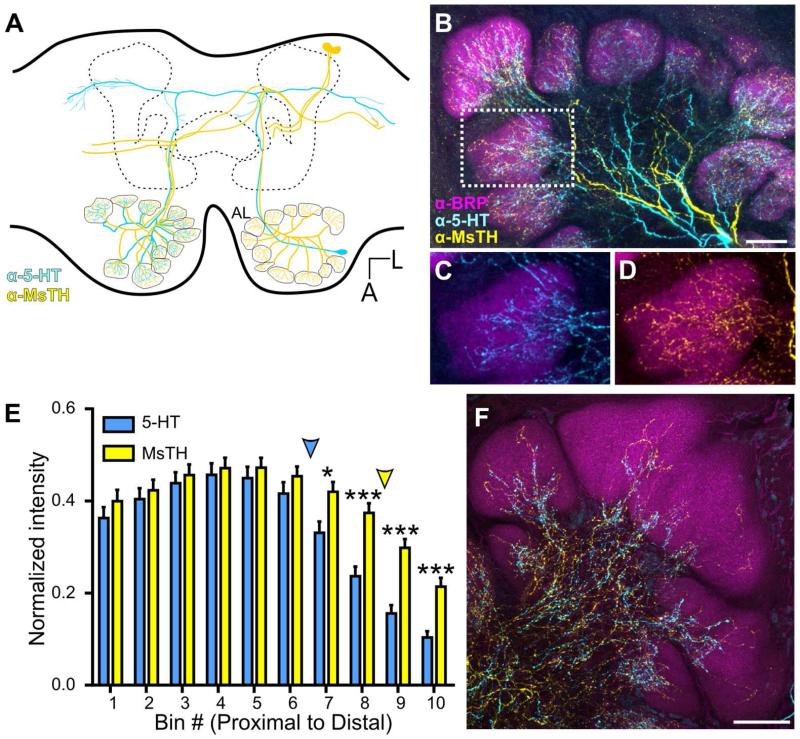
Figure 3.
Convergence of 5-HT-ir and MsTH-ir in AL glomeruli. A: Schematic of one pair of DAAR neurons (yellow) and a single CSD (blue) neuron within the brain of Manduca. The CSD cell bodies are located in the lateral cell cluster, while the DAAR cell bodies are located in the dorsal protocerebrum. Each AL is innervated by one CSD neuron which projects to the contralateral AL and innervates all glomeruli. Four DAAR neurons (one pair on each side of the brain) project to both the ipsilateral and contralateral ALs innervating all glomeruli. B: 5-HT-ir (cyan) is densely distributed near the proximal region of glomeruli while MsTH-ir (yellow) is distributed sparsely throughout glomeruli. Glomerular boundaries are delineated by BRP-ir (magenta). C, D: Inset from B depicting individual channels with 5HT-ir/BRP-ir and MsTH-ir/BRP-ir respectively. E: Glomerular distribution of 5-HT-ir and MsTH-ir along the proximal to distal axis of isomorphic glomeruli. MsTH-ir extends farther distally than 5-HT (Multiple t-tests; t= 2.76 for bin7, t=4.55 for bin 8, t= 5.44 for bin 9, t= 4.68 for bin 10; df=18; p=0.012 for bin 7p<0.0001 for bin 8-10; n=100). The distribution of each modulator began to significantly reduce in intensity along the proximal to distal axis at different points. For 5-HT, intensity values began to significantly decrease at bin 6 (1-way ANOVA; p<0.01, df=9, n=10), while for MsTH, the intensity values don’t begin to significantly decrease until bin 9 (1-way ANOVA; p<0.05, df=9, n=10). Colored arrowheads denote where the intensity of each modulator begins to significantly reduce. F: Macroglomerular complex (MGC) demonstrating sparse innervation of both 5-HT-ir and MsTH-ir. All scale bars = 50 um.