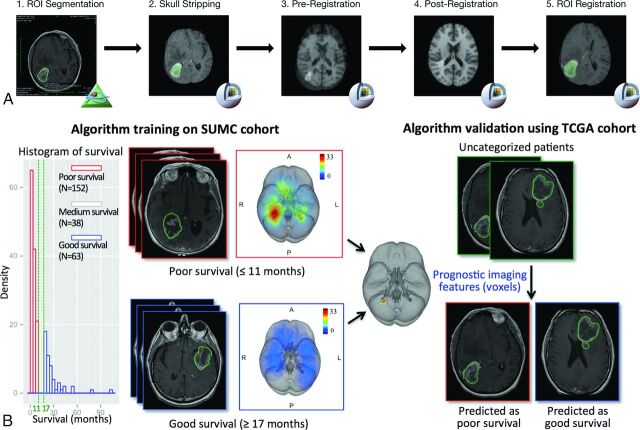
Fig 1.
An overview of the image-processing pipeline and model training and validation procedure to identify locations associated with survival. A, The image-processing pipeline is applied to both training (Stanford University Medical Center) and validation (TCGA) cohorts. B, Algorithm training identifies anatomic regions associated with survival, which is validated in the TCGA cohort. The training algorithm using the threshold-free cluster enhancement method takes as the input group labels dichotomized by survival outcome and the superimposed tumor heat map of the Stanford University Medical Center patient cohort analyzed in the image-processing pipeline; the pipeline outputs anatomic regions significantly associated with the 2 survival groups, which are used to classify the TCGA validation set into a poor survival group and a good survival group on the basis of tumor regions present or absent in the prognostic region.