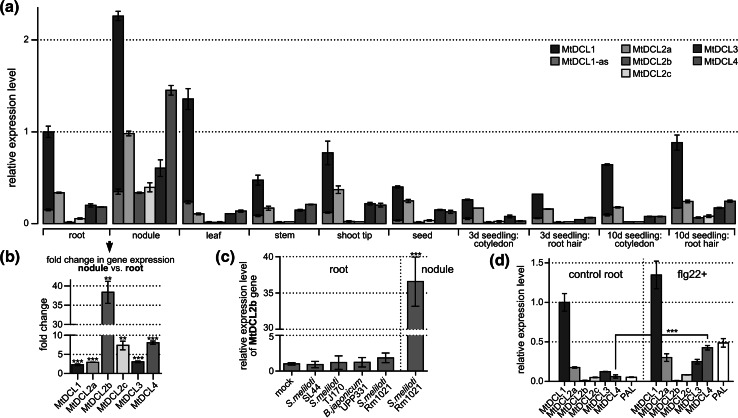
Fig. 2.
Expression profile of M. truncatula DCL genes. a Expression of MtDCL genes was examined with ddPCR in different parts of the plant: cotyledon (with hypocotyl) and root hair of 3- and 10-day-old seedling (seedl), mature leave, stem, shoot tip, root, nodule and seed. Additionally, accumulation of an alternative splicing variant with intron 14 retention (MtDCL1-as) that constitute a fraction of the total MtDCL1 mRNA was measured. Bars represent mean values ± SD of three biological replicates normalized to the expression of the β-actin gene. b The mean expression fold change ± SD of the six M. truncatula DCL genes in nodule compared to root. Asterisks denote significant upregulation of a particular gene in nodule in comparison to the level of its expression in root (**P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). c The levels of MtDCL2b expression in roots and nodules of plants treated with S. meliloti Rm1021 and in roots of plants treated with S. meliloti mutants SL44 and TJ170 and B. japonicum UPP331 strain. Bars represent mean values ± SD of three biological replicates normalized to the expression of the β-actin gene. Asterisks denote significant upregulation of MtDCL2b in nodule in comparison to root (***P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). d The levels of MtDCL expression in roots treated with flg22 peptide compared to mock-treated control. Bars represent mean values ± SD of three biological replicates normalized to the expression of the β-actin gene. Phenylalanineamonialyase (PAL) gene was used as a marker of the activation of plant defense responses. Asterisks denote significant upregulation of MtDCL4 under flg22 treatment (***P < 0.0001; paired t test)