Fig. 3.
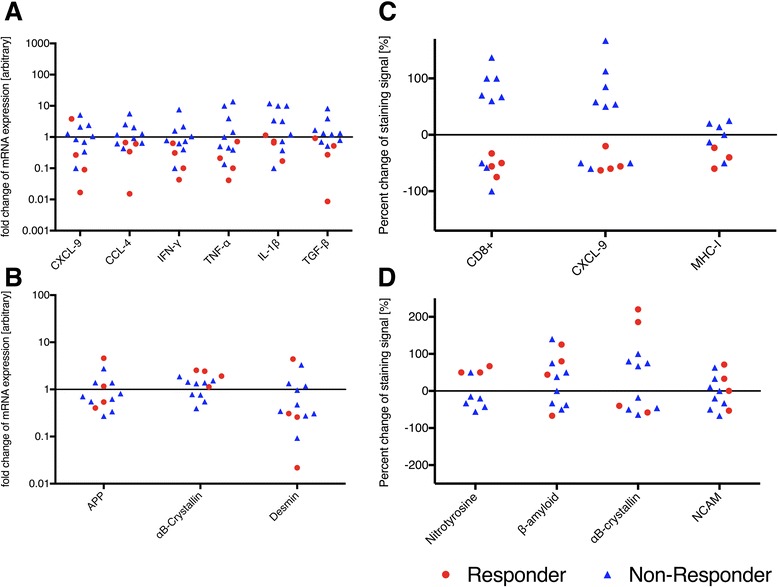
Change of expression of relevant markers measured with qPCR and immunohistochemistry. Mean fold reduction of qPCR assessment (a, b) and mean reduction in signal intensity (c, d) before versus after treatment for pro-inflammatory (a, c) and degeneration-associated molecules (b, d). Assessment of semiquantitative immunohistochemistry analysis was done by two masked observers of skeletal muscle biopsies stainings from all patients and the mean value is depicted. The group was divided into responders (red) and non-responders (blue). For pro-inflammatory molecules, one can assume a reduction in expression for responders (qPCR: p = 0.048 for CCL-4, p = 0.0403 for IL-1β; immunohistochemistry: p = 0.013 for CD8+, p = 0.0095 for CXCL-9, p = 0.042 for MHC-I), whereas non-responders show an increase of expression of proinflammatory molecules. Only one patient, who responded well to therapy, revealed an increase in CXCL-9 expression. In both groups, the change of expression of degeneration-associated molecules did not differ, regardless of the clinical improvement
