Figure 2.
EWS-FLI1-Dependent Small-Cell Osteosarcoma Model by Utilizing the Lentiviral EWS-FLI1 Expression System
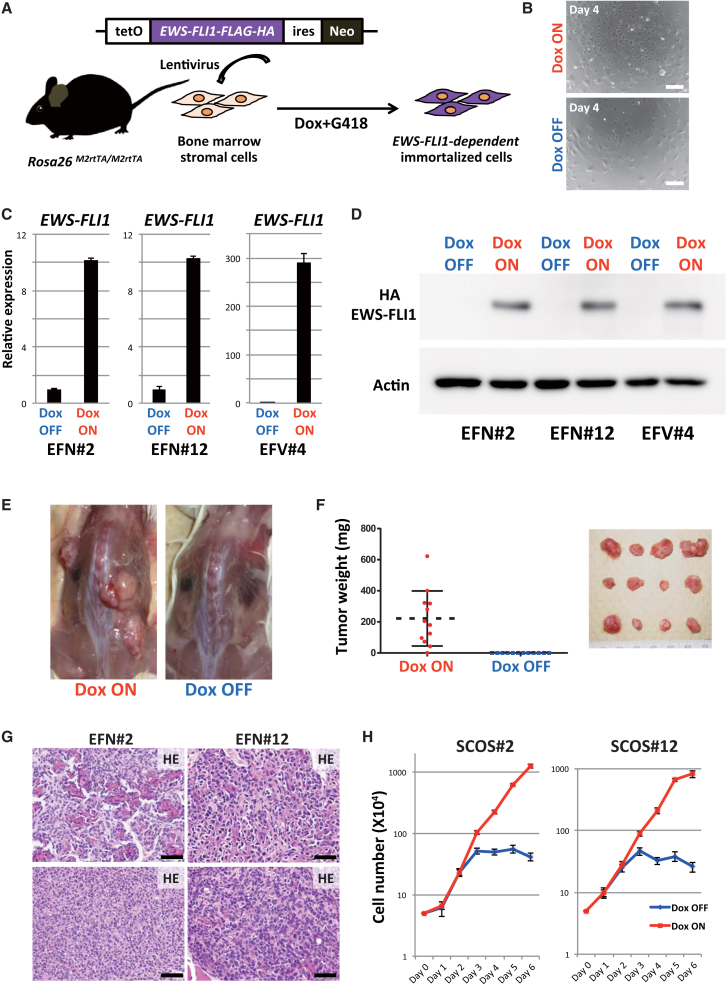
(A) Schematic illustrations of the lentiviral EWS-FLI1 expression system. Lentivirus was introduced into bone marrow stromal cells collected from Rosa26-M2rtTA mice. EWS-FLI1-expressing neomycin-resistant cells survived this protocol.
(B) The immortalized cells (EFN#2) grew rapidly in Dox-containing medium. Dox withdrawal resulted in growth retardation and morphological change in EWS-FLI1-expressing cells (4 days after the withdrawal). Scale bars, 200 μm.
(C) qRT-PCR results show EWS-FLI1 mRNA expression in Dox-treated samples (24 hr). Data are presented as means ± SD (three technical replicates). The expression level of Dox OFF cells was set to 1.
(D) Western blotting using anti-HA antibody detected EWS-FLI1 protein in the presence of Dox (48 hr).
(E) EWS-FLI1-dependent immortalized cells (EFN#2) developed tumors in immunocompromised mice only in the presence of Dox (10 weeks after the transplantation).
(F) Tumor weight at 10 weeks after the transplantation of EFN#2 with/without Dox administration. Tumor development depended on Dox administration (n = 12, independent samples for each group). Error bars represent SD.
(G) Histology of EWS-FLI1-induced tumors in immunocompromised mice. Tumors are small-cell osteosarcomas, which consist of small blue round cells with various amounts of osteoid formation. The osteoid-rich region (upper) and small blue round cell-rich region (lower) are shown. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(H) Cell growth assay of the established EWS-FLI1-dependent sarcoma cell lines (SCOS#2 and SCOS#12). The growth of sarcoma cells depended on EWS-FLI1 expression. Sarcoma cells without Dox exposure started to lose their growth at 3 days after Dox withdrawal. The means ± SD are shown in each group (two technical replicates per n; n = 3 biological replicates).