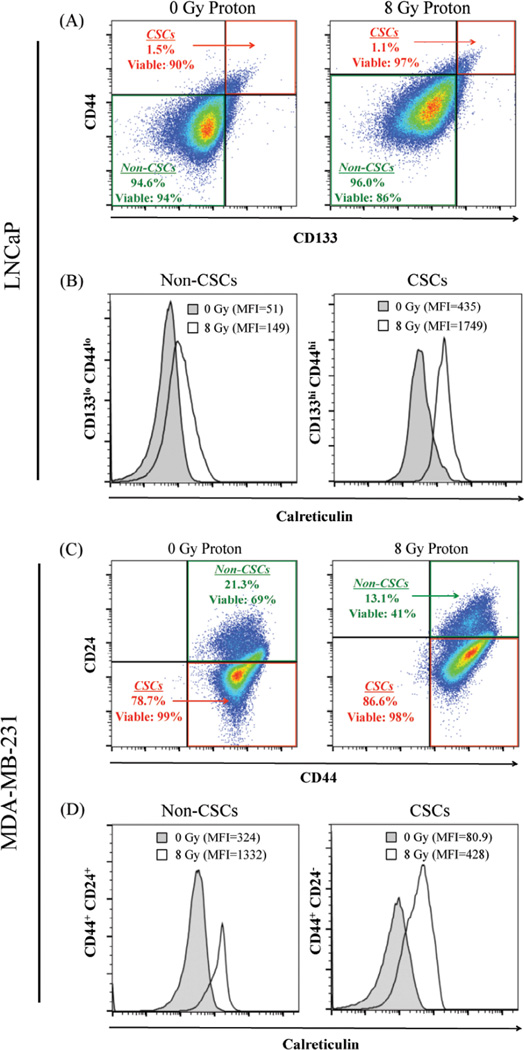
Figure 5. Residential CSCs exposed to proton radiation harbor increased calreticulin expression on the cell surface.
(A) Flow cytometry was utilized to identify the stem-like (CD133hi CD44hi, designated CSC) and non-stem-like (CD133lo CD44lo, designated non-CSC) cells in LNCaP populations 96 h after mock (0 Gy) or proton radiation (8 Gy). Insets: percentage and viability of each population. (B) Calreticulin cell-surface expression in non-CSC and CSC populations after mock (closed histograms) or proton (open histograms) radiation. (C) MDA-MB-231 stem-like (CD44+CD24−) and non-stem-like (CD44+CD24+) cell populations. Insets: percentage and viability of each population. (D) Cell-surface expression of calreticulin in non-CSC and CSC populations after mock (closed histograms) or proton (open histograms) radiation. Viability was examined using LIVE/DEAD Fixable Violet Dead Stain. Cell surface expression of markers was evaluated on live cells gated by FSC/SSC and LIVE/DEAD staining.