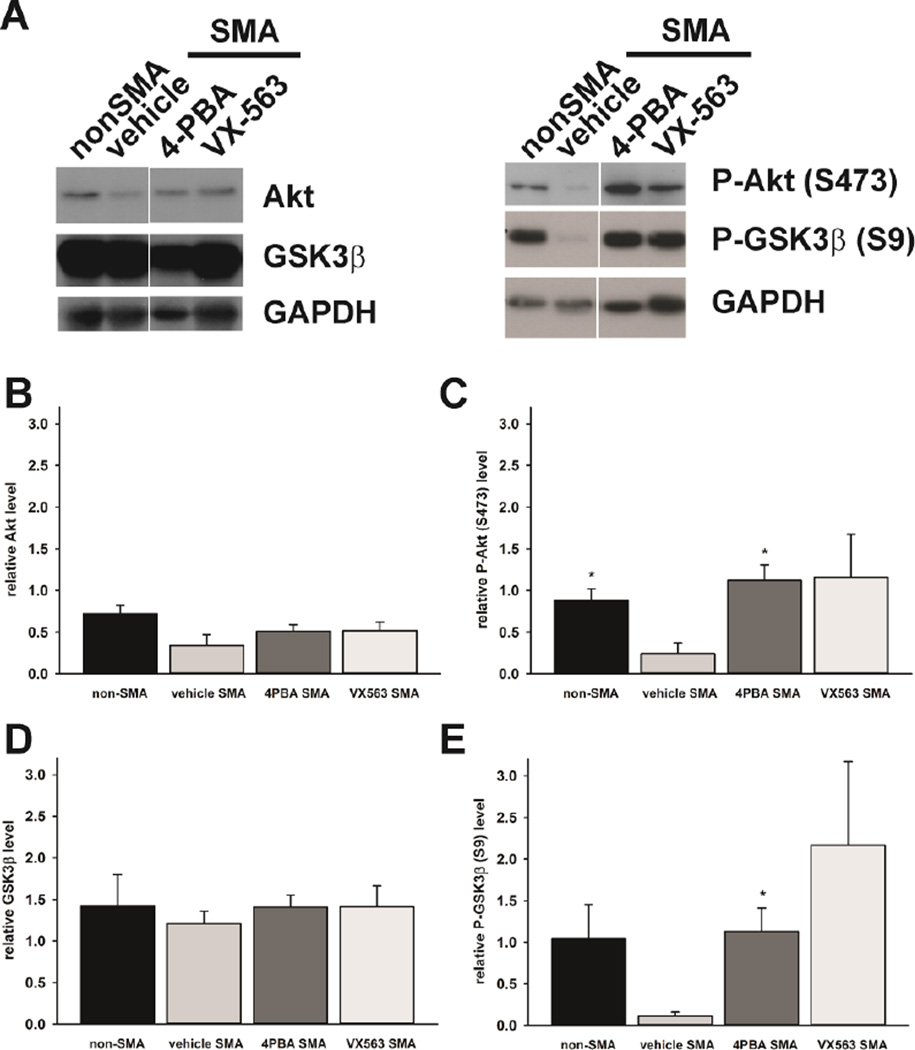
Figure 9. The effects of 4PBA and VX563 on Akt signaling in SMNΔ7 SMA mice.
SMNΔ7 SMA mice (n = 3/group) were treated with either 4PBA, VX563 or their appropriate vehicles for 5 days beginning at PND04. Age-matched non-SMA mice were also included as controls. The effects of these compounds on both the levels of and the phosphorylation of Akt and one of its substrates, GSK3β, were determined by immunoblot (A). The band intensities for each target protein were normalized against those for the loading control GAPDH. The levels of Akt protein (B) were not affected by disease status (compare non-SMA to vehicle SMA) or by drug treatment. The phosphorylation of Akt at serine 473 (S473) was reduced in the spinal cord of SMNΔ7 SMA mice (C). Treatment of these mice with either 4PBA or VX563 increased Akt phosphorylation. As with Akt, the levels of GSK3β protein (D) were not affected by disease status or by drug treatment. The phosphorylation of GSK3β at serine 9 (S9) was reduced in the spinal cord of SMNΔ7 SMA mice (E). Treatment of these mice with either 4PBA or VX563 increased GSK3β phosphorylation. The asterisk (*) denotes a statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) difference when compared to vehicle-treated SMNΔ7 SMA mice.