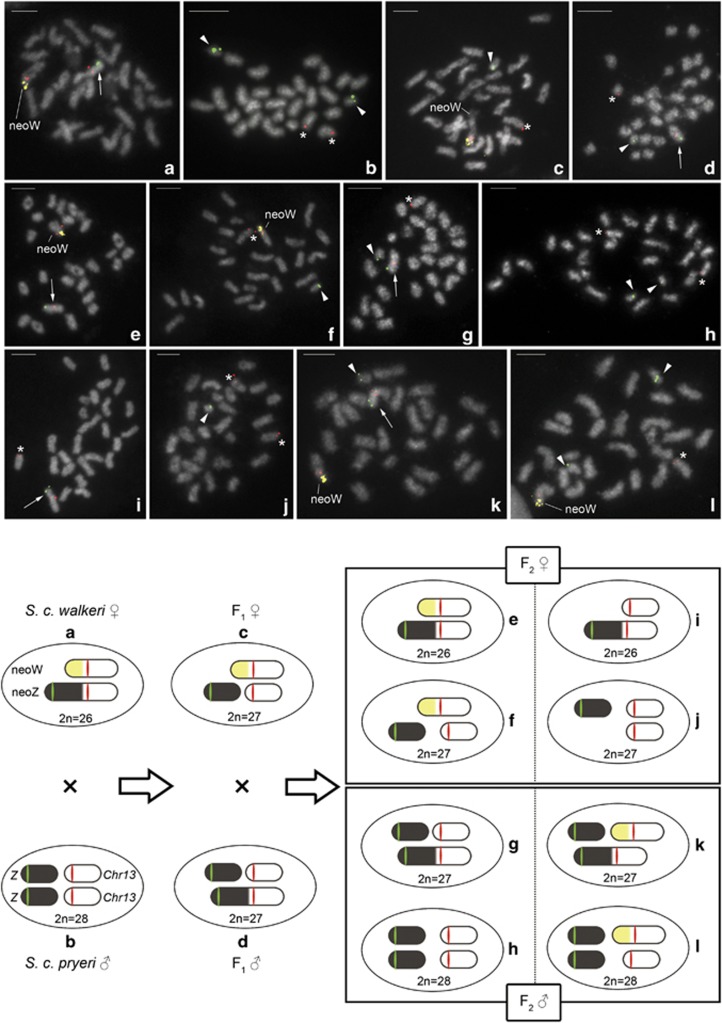
Figure 4.
Upper panel: FISH with sex chromosome-derived probes in mitotic metaphase complements of parents (a, b) and F1 (c, d) and F2 (e-l) offspring of crosses between Samia cynthia walkeri females and Samia cynthia pryeri males. Chromosomes were stained with DAPI (grey). Cy3-labelled probe of the 32B23 fosmid clone (red signals) mapped to chromosome 13 or the corresponding autosomal part of the neo-Z and neo-W chromosomes, and Green-labelled probe of the 45A6 fosmid clone (green signals) to the Z chromosome or the ancestral part of the neo-Z chromosome. Cy3-labelled W-painting probe (yellow signals) highlighted the ancestral part of the neo-W chromosome of S. c. walkeri. Bar=5.0 μm. Arrows, arrowheads, and asterisks indicate the neo-Z chromosome, Z chromosome and chromosome 13, respectively. (a) S. c. walkeri female, (b) S. c. pryeri male, (c) F1 female, (d) F1 male, (e, f, i, j) F2 females and (g, h, k, l) F2 males. Mitotic metaphase complements of F2 hybrids were examined in eight males and eight females (Supplementary Table S2). Lower panel: schematic illustrations of sex chromosome constitutions in parents and F1 and F2 hybrids from matings between S. c. walkeri females and S. c. pryeri males, based on the FISH results.