Figure 1. Regulation of AMPK Activity.
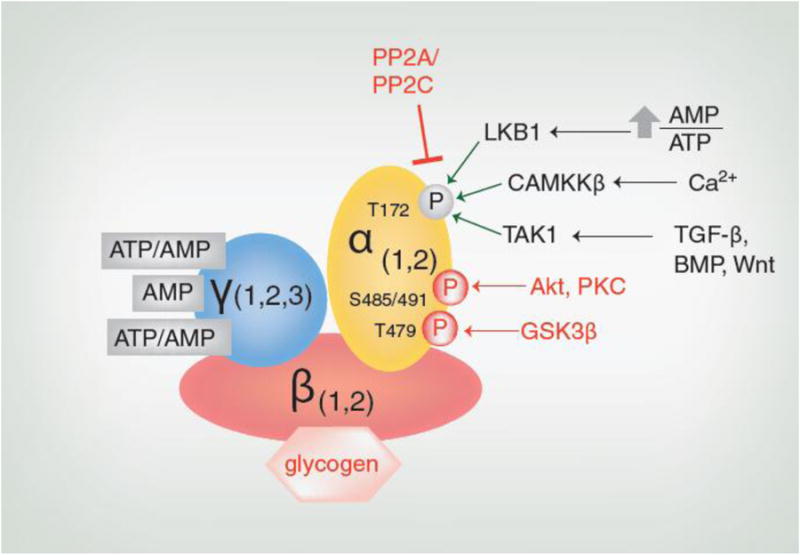
When the AMP/ATP ratio increases, tumor suppressor liver kinase B1 (LKB1) phosphorylates Thr172. Increases in intracellular calcium levels activate calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CAMKKβ), which also phosphorylates Thr172. Transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1 (TAK1) phosphorylates AMPK at Thr172 in response to signaling from transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), bone morphogenic protein (BMP) or Wnt. AMPK activity also depends on the activity of protein phosphatases such as PP2A and PP2C that target Thr172. In addition, AMPK activity may be inhibited by the binding of its β subunit to glycogen or the phosphorylation of its α subunit at Thr479 by glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) or Ser485 (α1)/Ser491(α2) by Akt and possibly other molecules including protein kinase C (PKC). Factors which inhibit AMPK activity are shown in red.
