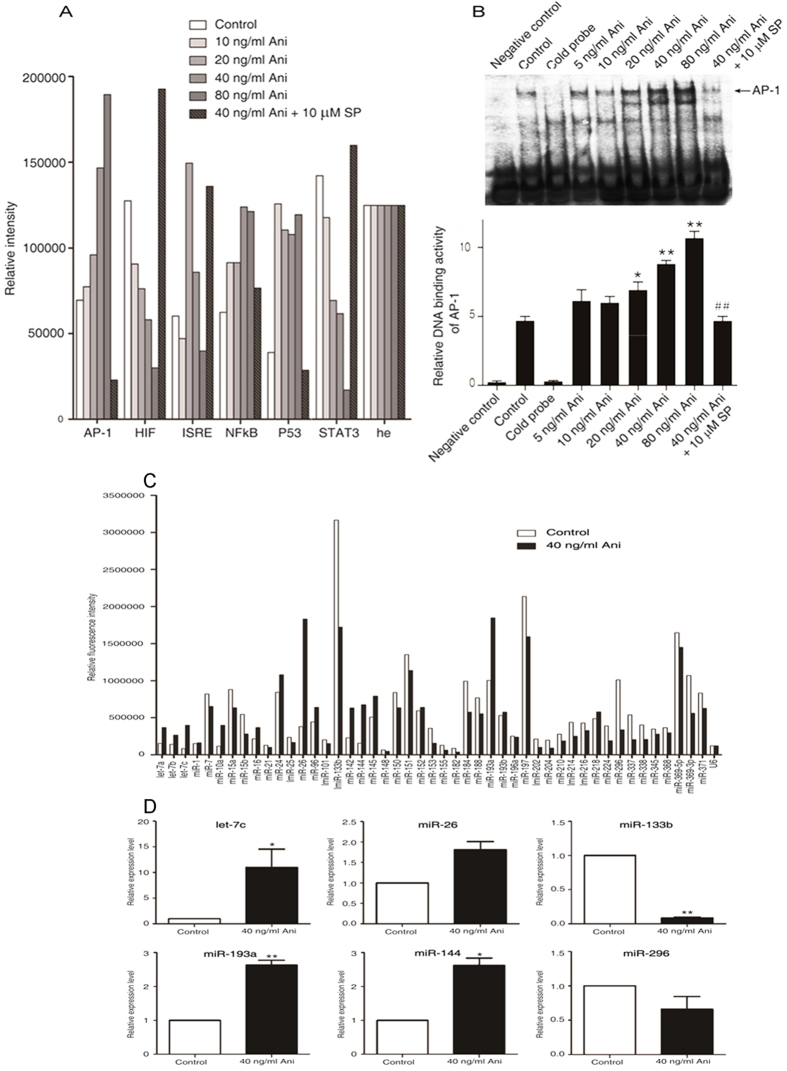
Figure 4. Anisomycin significantly increases the expression of miRNA let-7c in the JNK/AP-1-induced apoptosis of Jurkat T cells.
Two hours after pre-incubation with 10 μM SP600125, Jurkat T cells were treated with the increasing concentrations of anisomycin for 6 h (A,B). (A) The activities of the six apoptosis-associated transcriptional factors, AP-1, HIF, ISRE, NF-κB, P53 and STAT3, were measured using the TF Reporter Plate Array. (B) AP-1 DNA binding activity was tested by the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. On the other hand, the cells were treated with or without 40 ng/ml of anisomycin for 24 h (C,D). (C) miRNA plate array analysis for 47 apoptosis-associated miRNAs was performed with the RNA extracts from the treated Jurkat T cells. (D) The real-time quantitative PCR analysis of differentially expressed six miRNAs, including miR let-7c, miR-26, miR-133b, miR-193a, miR-144 and miR-296, was performed to further validate the microarray results. More than triplicate assays were carried out for each RNA sample. For the (A,B), the data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. the untreated control, ##p < 0.01 vs. the 40 ng/ml of anisomycin group. For the (C,D), The data are shown as the fold changes of the miRNA levels in the anisomycin-treated group relative to the control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.