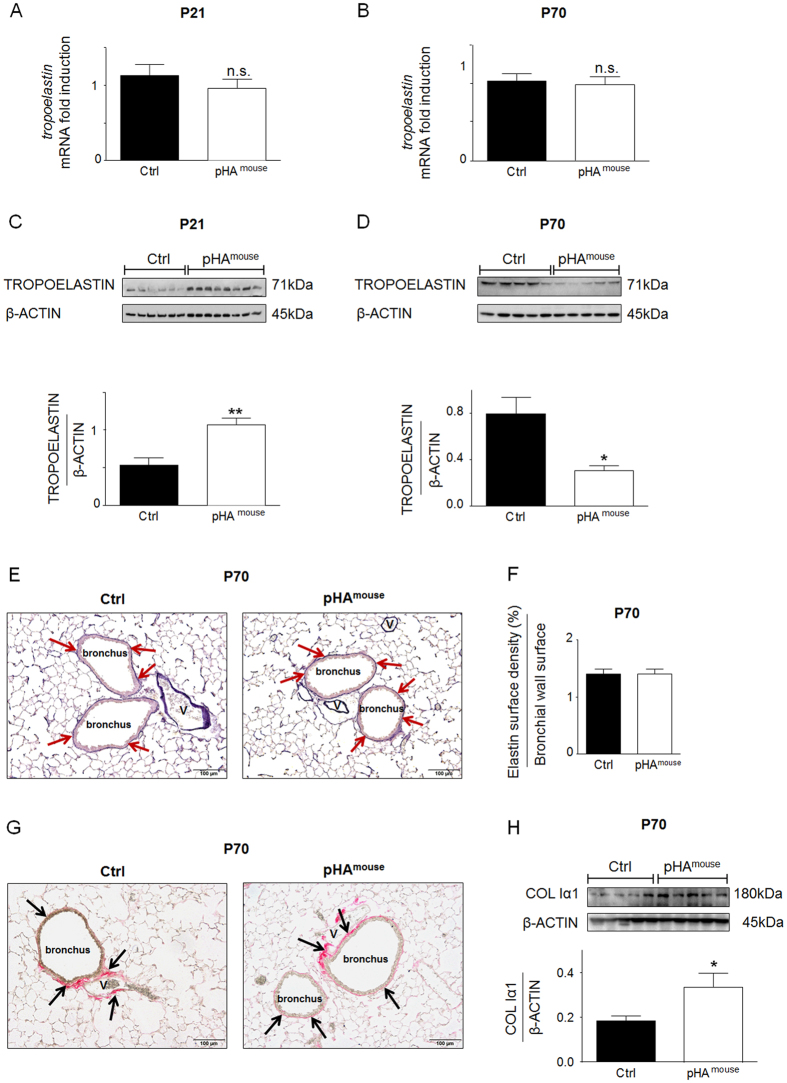
Figure 7. Early postnatal hyperalimentation (pHA) with early-onset obesity temporo dynamically regulates murine pulmonary elastin synthesis and induces greater collagen Iα1 protein abundance.
(A,B) Assessment of tropoelastin mRNA in total lung homogenate by quantitative qRT-PCR at postnatal day 21 (P21) (A) (Ctrl: n = 10 from 5 litters; pHAmouse: n = 10 from 6 litters) and at P70 (B) (Ctrl: n = 9–10 from 6 litters; pHAmouse: n = 10 from 6 litters). (C,D) Lung protein abundance of TROPOELASTIN at P21 (C) (Ctrl: n = 6 from 4 litters; pHAmouse: n = 8 from 4 litters) and at P70 (D) (Ctrl: n = 5 from 4 litters; pHAmouse: n = 5 from 4 litters). β-ACTIN served as loading Control (Ctrl). Densitometric analyses below the corresponding immunoblot. (E) Representative images illustrating elastic fibers using Hart’s staining in paraffin-embedded and paraformaldehyde-fixed lungs of the Ctrl-group (left panel) and of the pHAmouse-group (right panel) at P70. Red arrows are depicting positive staining of elastic fibers of the conducting airways (100–200 μm diameter). (F) Summary data of the quantification of positive elastic fiber staining surrounding the bronchi (100–200 μm) at P70. Elastin surface density was related to bronchial wall surface; pHAmouse group: n = 6 from 4 litterss, Ctrl: n = 6 from 5 litterss. (G) Representative images illustrating sirius-red staining used to visualize connective tissue of the peribronchial area (black arrows); pHAmouse group: n = 6 from 4 litterss, Ctrl: n = 6 from 5 litterss. (H) Immunoblot showing protein abundance of collagen Iα1 (COL Iα1) at P70. β-ACTIN served as loading Control (Ctrl); Ctrl: n = 5 from 4 litters; pHAmouse: n = 5 from 4 litters. Early postnatal hyperalimentation (pHAmouse group) compared to the Ctrl (Ctrl). pHAmouse group: white bar; Ctrl: black bar. Mean ± SEM; Mann Whitney test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; n.s. = not significant.