Figure 1. Activities of the plasma membrane redox system .
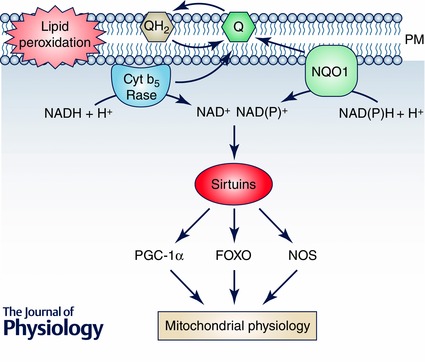
The Q‐dependent enzymatic activities at the plasma membrane (PM) not only prevent oxidative damage affecting lipid peroxidation through reduced Q or by maintaining vitamin E turnover in the membrane, but can also show other regulatory activities in the cytosol. The oxidation of NADH or NAD(P)H in the PM environment can regulate the activity of NAD+‐dependent deacetylases such as sirtuins, mainly SIRT1. These sirtuins will further regulate the activity of many other proteins involved in the control of metabolism and mitochondrial turnover such as PGC‐1α, FOXO or NOS among others. These proteins are involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, turnover and oxidative activity. Thus, upregulation of PMRS by CR in old animals can be linked to a higher SIRT1 activity and the regulation of mitochondrial function in old animals.
