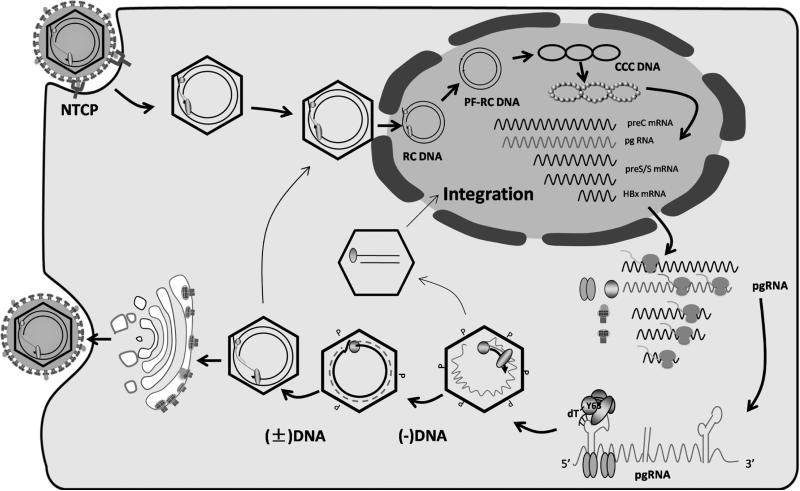
Fig. 1.
HBV life cycle. HBV enters hepatocytes through NTCP, followed by uncoating, and nuclear transport of the RC DNA. The RC DNA is converted to cccDNA, which serves as the template for transcription of the 3.5 kb preC RNA and pgRNA, 2.4- and 2.1-kb preS/S mRNAs, and 0.7-kb HBx mRNA. These RNAs are exported to cytoplasm for protein translation. pgRNA is selectively packaged inside core particles, followed by P protein-mediated (−) strand DNA synthesis (reverse transcription), pgRNA degradation, and (+) strand DNA synthesis to generate RC DNA. Such mature core particles can be enveloped for release as virions, or transported to the nucleus to generate more cccDNA. Double stranded linear DNA is an aberrant replication product of pgRNA, and the preferred template for integration into host chromosomal DNA.