Figure 3. Reaction catalyzed by MoaA.
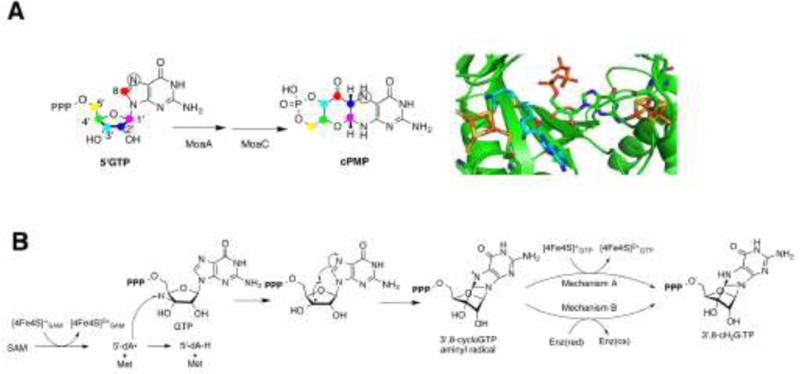
A) The conversion of 5′GTP to cPMP is catalyzed by MoaA and MoaC. The results of the isotope tracer experiments showed that all carbon atoms of the 5′GTP are found within cPMP. The C8 atom from the guanine ring is inserted between the C2′ and C3′ atoms of the ribose. The model of the active site of MoaA shows the binding of SAM (shown in light blue) (PDB ID: 1TV8) [38] and GTP (PDB ID: 2FB3) [37]. Oxygens are shown in red, nitrogens in blue, sulfurs in yellow, phosphorous in orange, and irons in brown. B) In the reaction catalyzed by MoaA, SAM is reductively cleaved to the 5′-dA• radical and L-methionine (Met) by oxidizing [4Fe-4S]SAM. The 5′-dA• then abstracts the H-3′ atom of GTP, resulting in the C3′ centered radical which attacks the C8 of the guanine to forms an aminyl radical intermediate. This intermediate is then reduced to form the 3′,8-cH2GTP intermediate. Two possible mechanisms of aminyl radical reduction are shown. In the mechanism A, [4Fe-4S]GTP cluster is the electron donor. In mechanism B, the electron is provided by an exogenous donor; an uncharacterized redox enzyme (Enz) in vivo.
