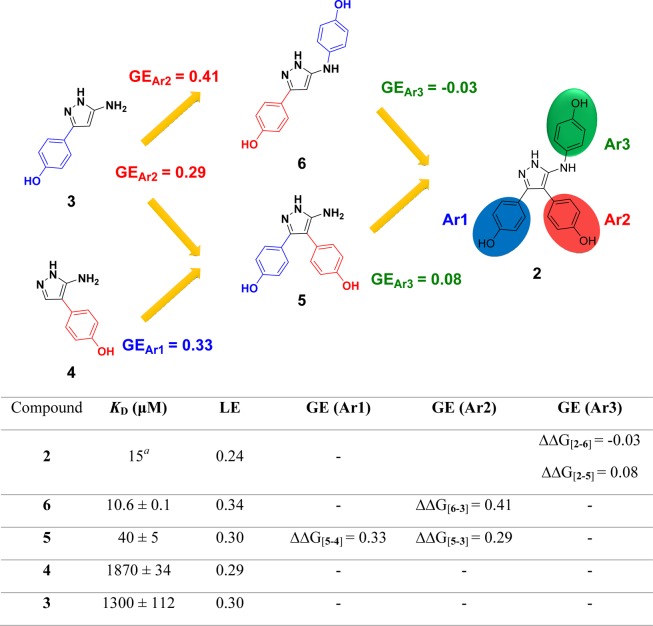
Figure 3.
Deconstruction of lead compound 2 into retrosynthetic fragments 3–6 was used to assess the binding affinity, ligand efficiency (LE), and group efficiency (GE) contribution of the individual components. The three aromatic rings decorating the aminopyrazole core of lead compound 2 have been labeled Ar1, Ar2, and Ar3 as illustrated, which refers to the orientation the rings occupy in the X-ray crystal structure of 2 in complex with CYP121 (Figure 1). Retrofragments 3 and 4 represent Ar1 and Ar2, respectively. The lower panel tabulates the binding affinity (KD) and LE and GE properties of compounds from the sequential reconstruction of lead 2 from component monoaryl (3 and 4) and biaryl (5 and 6) retrofragments. KD values were determined using ITC. LE was calculated from the Gibbs free energy of binding divided by the number of heavy atoms (ΔG/HA).29,30 GE contributions of the three aromatic rings Ar1, Ar2, and Ar3 were calculated from the change in Gibbs free energy per added heavy atom (−ΔΔG/ΔHA) as the retrofragments were progressively recombined to form lead compound 2.31KD previously reported.28