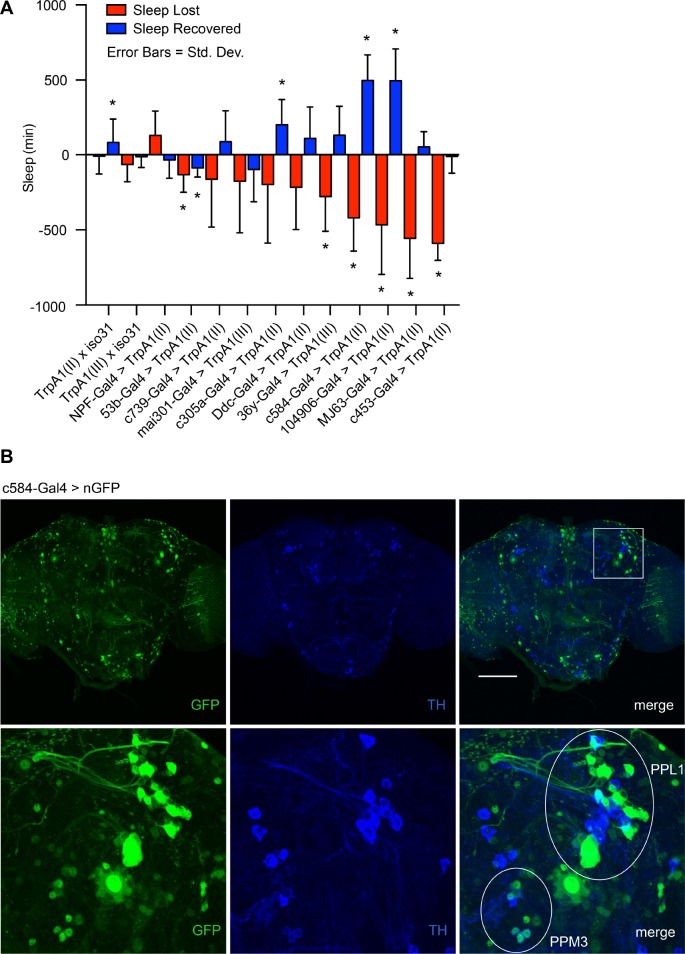
Figure 1.
Development of a novel thermogenetic tool to induce sleep deprivation and rebound in Drosophila. (A) Gal4 lines were screened to identify drivers that produce strong sleep loss and subsequent rebound when coupled with the heat-activated cation channel TrpA1. Each candidate Gal4 driver was paired with a UAS-TrpA1 transgene on the same chromosome as the Gal4 driver. A full day of baseline data were collected at 21°C, followed by 24 h of TrpA1 activation at 28°C (ZT0-ZT24) and a subsequent recovery day where flies were returned to 21°C. Error bars represent standard deviation. Significance was assessed with a one-sample Student t-test with a Bonferroni correction for multiple testing. P = 0.05. n = 11–52 per genotype. (B) GFP expression in c584-Gal4/UAS-nGFP flies shows relatively sparse expression in the brain driven by c584-Gal4. Immunohistochemistry with anti-TH and anti-GFP antibodies reveals clustering and costaining of c584-expressing neurons with dopaminergic neurons. GFP expression in c584-Gal4/UAS-nGFP flies includes non-dopaminergic neurons around the dopaminergic PPL1 cluster and co-staining with TH in neurons of the PPM3 cluster. Scale bar = 100 μm. ZT, Zeitgieber Time.