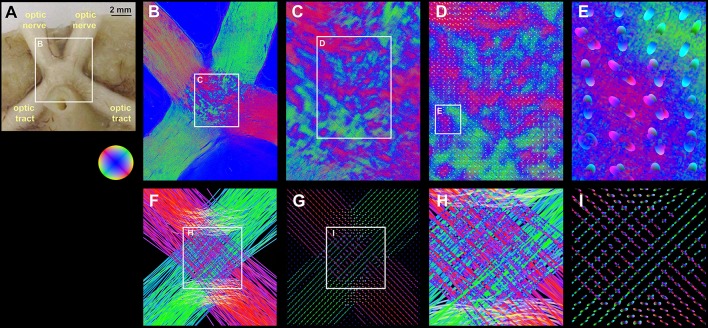
Figure 5.
Real and simulated brain section from the hooded seal. (A) Blockface image of the optic chiasm of the hooded seal before sectioning. (B) Fiber orientation map of a medial section through the optic chiasm. Optic nerves and optic tracts appear as massive and rather homogeneous fiber bundles. Most fiber tracts from the optic nerves decussate to the contralateral optic tract. (C) The decussation zone in the center (i.e., the chiasm) is characterized by a patch pattern produced by small fiber tracts (red and green color; exemplary orientations are indicated by black lines) and fiber crossings characterized by signal attenuation (blue color; exemplary highlighted by white arrow). Based on this FOM, pliODFs were created for super-voxel dimensions of 40 × 40 × 1 native voxels. (D,E) demonstrate different enlargements of the field of pliODFs overlaid with the input FOM. (F) FOM of a simulated section through the optic chiasm and (G) corresponding pliODFs for super-voxel dimensions of 40 × 40 × 1 native voxels. (H) Zoom into the FOM of the fiber decussation zone and (I) corresponding pliODFs. The effects of crossing and bending fibers on the ODF shapes are obvious.