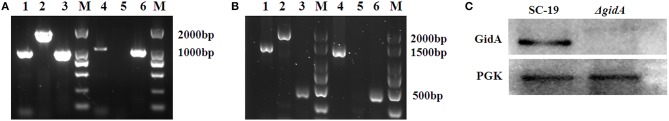
Figure 1.
Confirmation of the isogenic mutant ΔgidA. (A) Combined PCR analyses of the ΔgidA mutant. Lanes 1 and 4 represent the amplification of the upstream border of gidA using the primer set Gup-F and Gup-R. Lanes 2 and 5 represent the amplification of gidA using the primer set GidA-F and GidA-R. Lanes 3 and 6 represent the amplification of the downstream border of gidA using the primer set Gdown-F and Gdown-R. Lanes 1–3 use genomic DNA of SC-19 as templates, whereas Lanes 4–6 use genomic DNA of ΔgidA as templates. (B) Confirmation of the ΔgidA mutant by RT-PCR. Lanes 1 and 4 represent the amplification of downstream gene of gidA using the primer set 2162-F and 2162-R. Lanes 2 and 5 represent the amplification of gidA using primer set GidA-F and GidA-R. Lanes 3 and 6 represent the amplification of upstream gene of gidA using the primer set 2164-F and 2164-R. Lanes 1–3 use cDNA of SC-19 as templates, whereas Lanes 4–6 use cDNA of ΔgidA as templates. (C) Confirmation of the ΔgidA mutant by Western blot analysis. The supernatant of cell lysate from SC-19 and ΔgidA was disposed for immunoblot analysis with GidA or PGK polyclonal antibodies. An antibody directed against PGK was used as loading control.