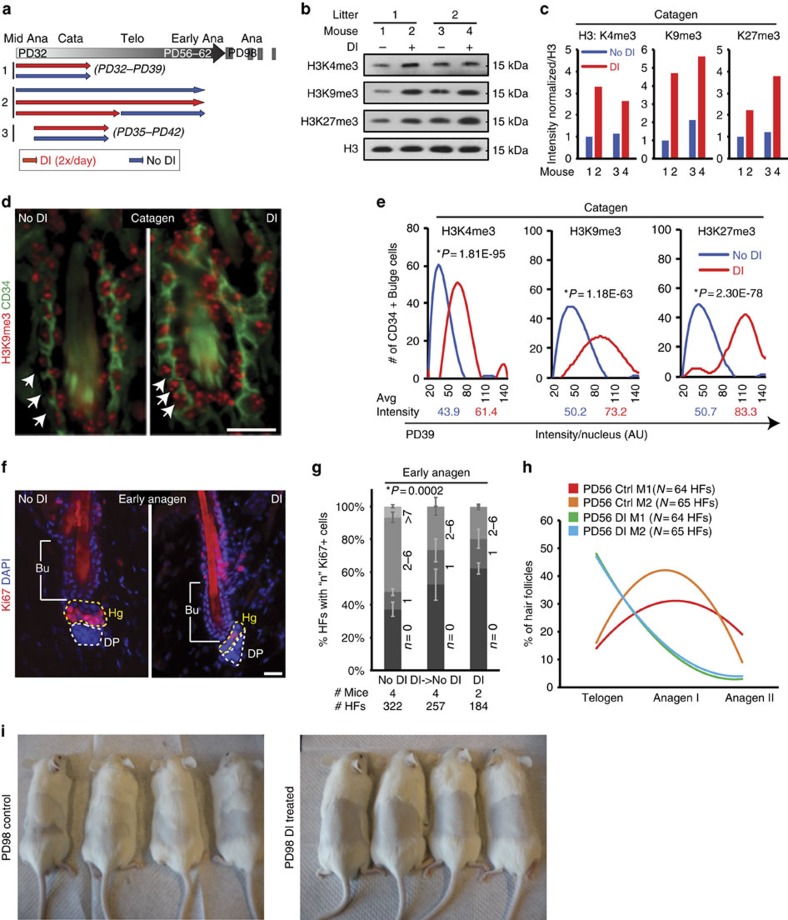
Figure 7. The level of histone H3 K4/K9/K27me3 in the skin is important for hair homeostasis.
(a) Experimental scheme of using demethylase inhibitors (DIs). (b,c) Western blot (b) and quantification of band intensity (c) of histone methylation from whole skin chromatin extracts of control and DI-treated mice. Band intensities were normalized to H3 signal. (d) Immunofluorescence staining of control and DI-treated (scheme 1 of (a)) hair follicle sections labelled with H3K9me3 (red) and CD34 (green). Scale bar, 20 μm. (e) Fluorescence intensity of all three marks from immunostainings were quantified for each bulge cell (CD34+). Student's t-test was used to determine statistical significance between control and DI-treated mice for each mark. (f) Immunofluorescence staining with a proliferation marker Ki67 of control and DI-treated (scheme 2 of a) skin sections. Scale bar, 20 μm. (g) The number of Ki67+ cells in f in each hair follicle were counted, and they showed reduced proliferation in DI-treated mice compared with control. The differences across the conditions were significant according to a Student's t-test. (h) Hair follicles of control and DI-treated mice were categorized in their hair cycle stages. Notice a dramatic increase in the number of telogen (Telo) hair follicles and reduction in anagen (Ana) I and II in DI-treated mice. (i) Mice were shaved, treated with DI in catagen (Cata; PD35–42; a, scheme 3), and followed long-term to monitor the hair cycle re-entry. Notice that mice in the control group show hair growth, whereas mice in DI-treated group show no growth. Avg, average.