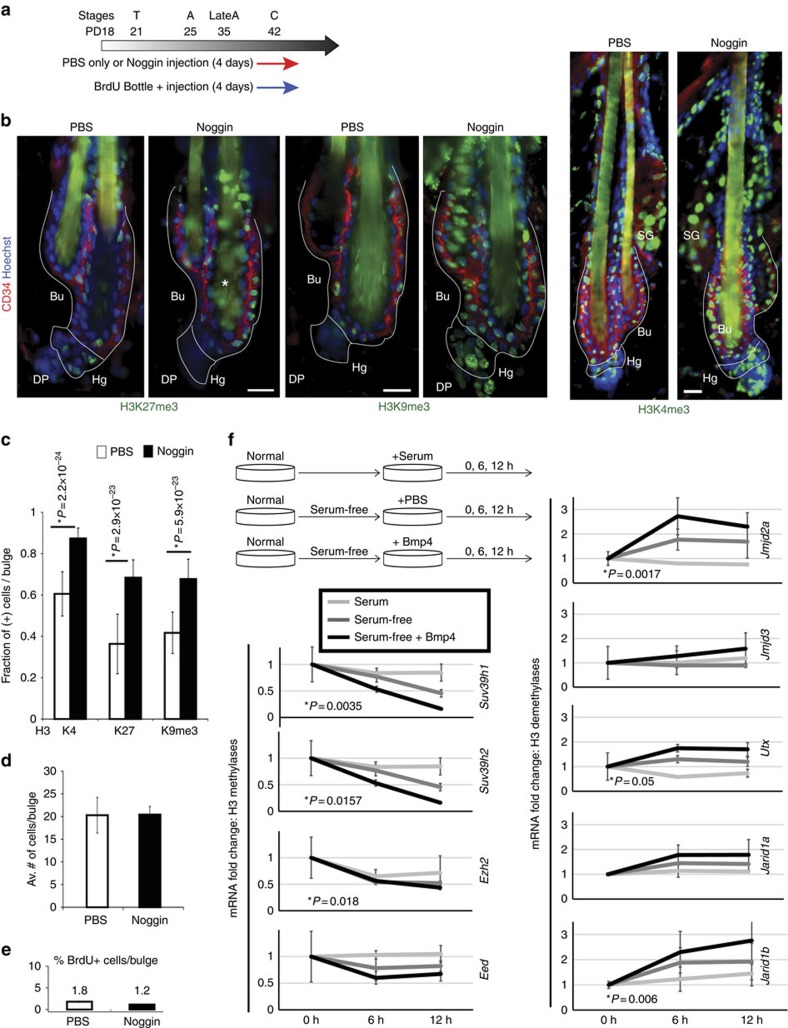
Figure 8. BMP signalling is involved in control of the global histone marks level.
(a) Noggin- or PBS-coated fluorescent microbeads were intradermally injected for 4 days in late catagen. BrdU was fed to mice in the water bottles to continuously label proliferating cells. (b) Representative images of immunofluorescence skin staining showing increased of methylation marks in Noggin-injected mice. Scale bars, 10 μm. (c) Quantification of methylation signal in bulge cells show a significant increase in cells positively bearing histone marks in Noggin-injected (black bar) mice relative to PBS control (white bar) mice (n=2 mice, N>40 hair follicles per condition, Student's t-test). (d,e) Quantification of number of CD34+ cells per bulge (d) and BrdU+ cells per bulge (e) after 4 days of injection shows no significant differences between Noggin and PBS control, suggesting lack of proliferation of bulge cells. N=2 mice per condition, n=20–40 hair follicles per mouse. (f) qRT–PCR of selected histone methylases and demethylases in keratinocytes cultured under serum (white line), serum-free (grey line) or serum-free+BMP4 (black line) conditions. Note the reduced expression of methylases and increase of demethylases upon BMP4 addition. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test. Results for all genes tested are shown in Supplementary Fig. 4b.