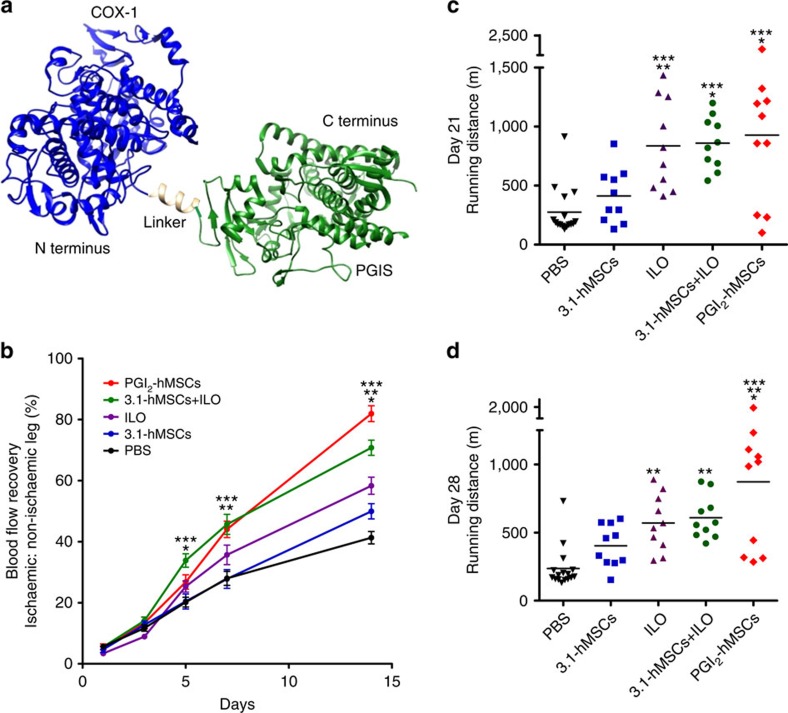
Figure 1. PGI2-hMSC therapy concurrently improved distal perfusion and treadmill performance after hindlimb ischaemia.
(a) Schematic cartoon illustration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS fusion protein. A His–Ala–Ile–Met–Gly–Val–Ala–Phe–Thr–Trp peptide linker (from a helical transmembrane domain of bovine rhodopsin) was used to connect the chimeric protein and to maintain the topology of both COX-1 and PGIS proteins. Structures used for generation of the schematic included PDB 3N8Z (COX-1)33, PDB 2IAG (PGIS)34 and PDB 1GZM (rhodopsin)35. (b) Quantitative analysis of perfusion from ankle to toe showed different rates of blood flow recovery among the five treatment groups over the 14-day observation period. Notably, at day 14 after cell administration, perfusion in the PGI2-hMSC group exceeded that in the four other treatment groups, leading to significantly better perfusion recovery. Day 5: *P<0.05 for 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus ILO or versus PGI2-hMSCs; ***P<0.001 for 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus 3.1-hMSCs or versus PBS. Day 7: **P<0.01 for 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus 3.1-hMSCs; PGI2-hMSCs versus 3.1-hMSCs. ***P<0.001 for 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus PBS; PGI2-hMSCs versus PBS. Day 14, *P<0.05 for 3.1-hMSCs versus PBS, ILO versus 3.1-hMSCs; **P<0.01 for 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus ILO, PGI2-hMSCs versus 3.1-hMSCs+ILO; ***P<0.001 for ILO versus PBS, 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus PBS or versus 3.1-hMSCs, PGI2-hMSCs versus PBS or versus ILO or versus 3.1-hMSCs. (c) In run-to-exhaustion tests, mice treated with PGI2-hMSCs, daily injections of ILO or 3.1-hMSCs+ILO had a significantly longer maximal running distance than those treated with 3.1-hMSCs or vehicle (PBS) at 21 days. *P<0.05 for PGI2-hMSCs versus 3.1-hMSCs; 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus 3.1-hMSCs. **P<0.01 for ILO versus 3.1-hMSCs; ***P<0.001 for ILO versus PBS; 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus PBS; PGI2-hMSCs versus PBS. (d) At 28 days, the performance enhancement in PGI2-hMSC-treated mice was similar to that seen at day 21. Meanwhile, 3.1-hMSCs+ILO outperformed ILO treatment when compared with 3.1-hMSC treatment (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test). *P<0.05 for PGI2-hMSCs versus ILO or versus 3.1-hMSCs+ILO. **P<0.01 for ILO versus PBS, 3.1-hMSCs+ILO versus PBS, PGI2-hMSCs versus 3.1-hMSCs. ***P<0.001 for PGI2-hMSCs versus PBS. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc test. Data are shown as mean±s.e.m. N=16 of sex-matched mice in vehicle (PBS) group; N=10 sex-matched mice each in the other four treatment groups.