Figure 2.
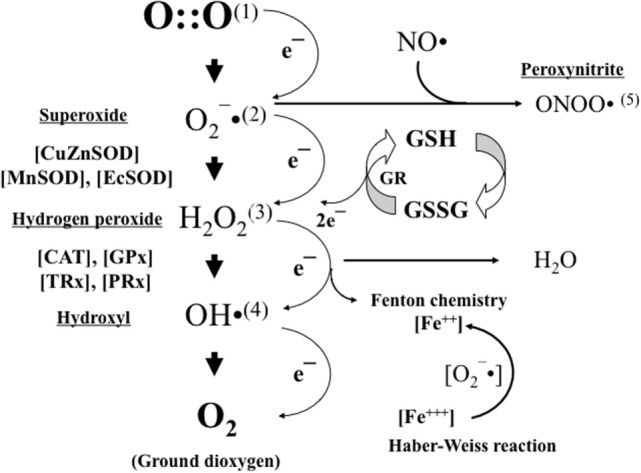
Oxygen (1) is stepwise reduced by just one electron leading to the formation of anion superoxide (2). Anion superoxide is dismutated by superoxide dismutases (SODs) to hydrogen peroxide (3), which in turn is transformed into water and oxygen by the action of catalases (CATs) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX). In the presence of transition metals (e.g., iron and copper), hydrogen peroxide can be transformed into hydroxyl radical (4). Moreover, in the presence of nitric oxide (NO), anion superoxide can also be transformed into peroxynitrite (5). Anion superoxide, hydroxyl radical, and peroxynitrite are highly reactive free radicals that will cause structural and functional damage to nearby standing molecules. Hydrogen peroxide will act as a cell-signaling molecule. Reduced glutathione (GSH) is the most relevant non-enzymatic antioxidant in the cell cytoplasm and an essential determinant of cell’s redox balance.
