Figure 5.
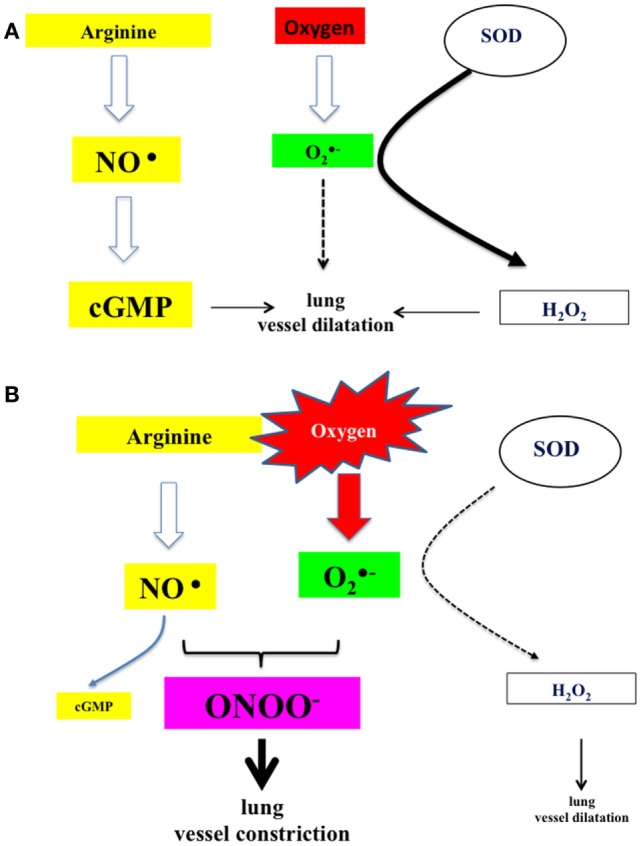
(A) Under normal circumstances, nitric oxide produced by the action of NO synthase activates guanylate cyclase, which catalyzes the formation of cGMP and subsequently lung vessel vasodilatation. In addition, superoxide anion, derived from air-borne oxygen by the action of superoxide dismutases, is catalyzed to hydrogen peroxide, which acts also as lung vessel vasodilator. (B) In the presence of oxygen in excess (resuscitation and ventilation), anion superoxide will sequester nitric oxide and produce highly reactive peroxynitrite. The amount of available cGMP is reduced and also the production of hydrogen peroxide. Under these circumstances, there is a potent tendency toward vasoconstriction (17, 25, 27).
