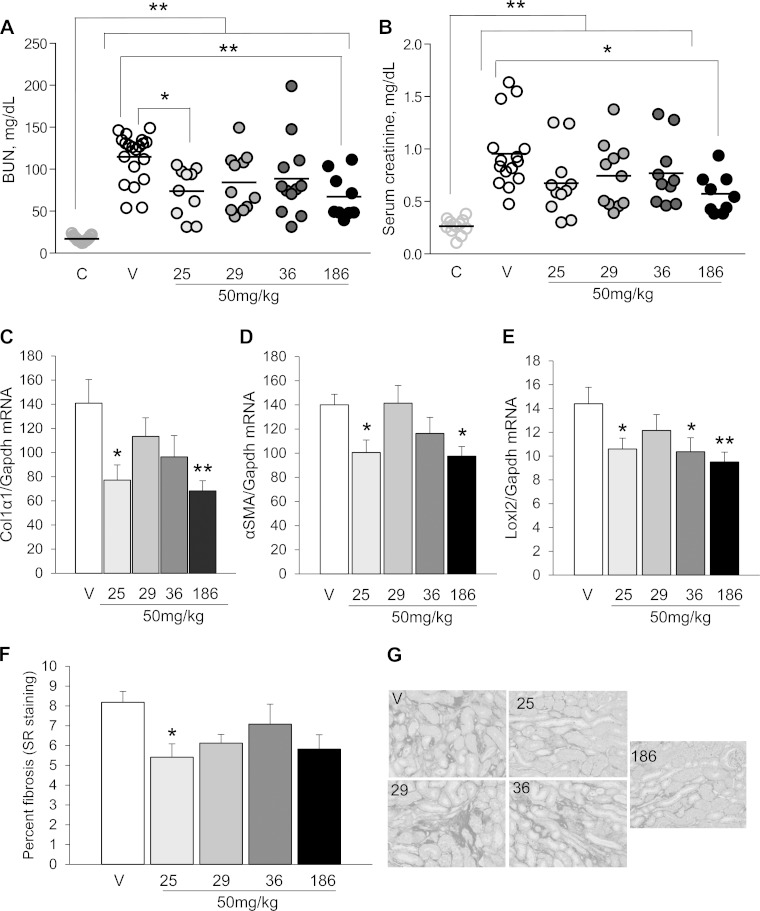
Fig. 4.
UPHD25 and 186 accelerate functional recovery and postinjury fibrosis after IR-AKI. Male BALB/c mice underwent left-sided renal pedicle clamping for 31 min to induce IR-AKI and were treated with vehicle or 50 mg/kg UPHD25, 29, 36, or 186 ip daily for 7 days starting 24 h after injury. A and B: functional recovery. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN; A) and serum creatinine (B) were measured at day 9, 1 day later after right nephrectomy to assess functional recovery (nos. of mice for A and B: uninjured mice, n = 12/15, day 9 after injury; vehicle controls, n = 20/15; UPHD25, n = 10/11; UPHD29, n = 11 each; UPHD36, n = 12/10; UPHD186, n = 9 each). Individual data points and means for each group are shown. C–G: renal fibrosis 28 days after IR-AKI. C–E: expression of renal fibrosis markers Col1α1, α-SMA, and LoxL2 mRNA relative to Gapdh mRNA control. F and G: Sirius red staining for interstitial collagen. F: quantification of Sirius red staining (% total area). G: representative images for Sirius red-stained tissues (outer medulla; scale bars = 50 μm). C–G: nos. of mice: vehicle controls, n = 11; UPHD25, n = 11; UPHD29, n = 11; UPHD36, n = 10; UPHD186, n = 10. Values are means ± SE. We performed 1-way ANOVA (P < 0.05) with Dunnett's correction for multiple between-group testing. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. uninjured control or vs. injured vehicle control, as indicated; C–F vs. vehicle control only.