Figure 7.
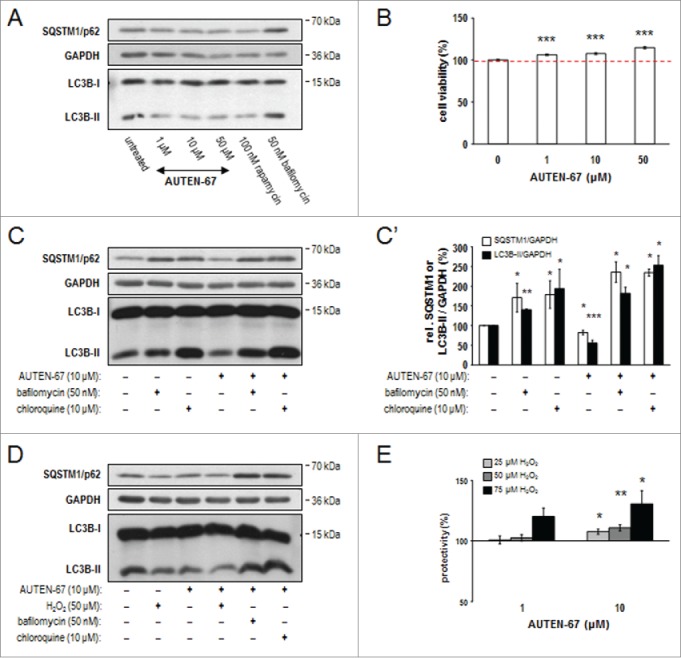
AUTEN-67 induces autophagic flux and increases viability in neurons. (A) Western blotting demonstrates relative SQSTM1/p62 and LC3B-II protein levels in murine primary neuronal cell cultures. Similar to rapamycin treatment, AUTEN-67 decreases the level of both proteins. LC3B-I levels remain nearly constant. (B) AUTEN-67 increases viability of isolated neurons in a concentration dependent manner. The dashed red line indicates mean relative viability of untreated control cells (100%). Survival of cortical neurons from a 7-d-old cell culture prepared from a 15-d-old mouse embryo is significantly increased in response to AUTEN-67 treatment. Survival rate was determined by the MTT method (see Materials and Methods). Data represent the results of 5 independent treatments. Bars represent s.e.m. For each treated sample, P < 0.001 (Student t test). (C) Relative levels of SQSTM1/p62 and LC3B-II proteins (western blot). AUTEN-67 decreases the level of both proteins only in the absence of autophagy inhibitors (Baf and chloroquine). (C') Quantification of band intensities from relevant western blots. Bars represent s.e. *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01: ***: P < 0.001, compared to control values (unpaired t test). (D) Western blot analysis showing relative SQSTM1/p62 and LC3B-II levels. AUTEN-67 increases autophagic flux in isolated neurons exposed to oxidative stress. (E) AUTEN-67 strongly enhances the viability of isolated neurons exposed to H2O2 treatment. Survival rates were determined by the MTT method. Data represent relative changes to cells treated with H2O2 only (control). Columns display the results of 4 independent treatments. Bars represent s.e. (Student t test). On panels A, C and D, GAPDH serves as control.
