Figure 2.
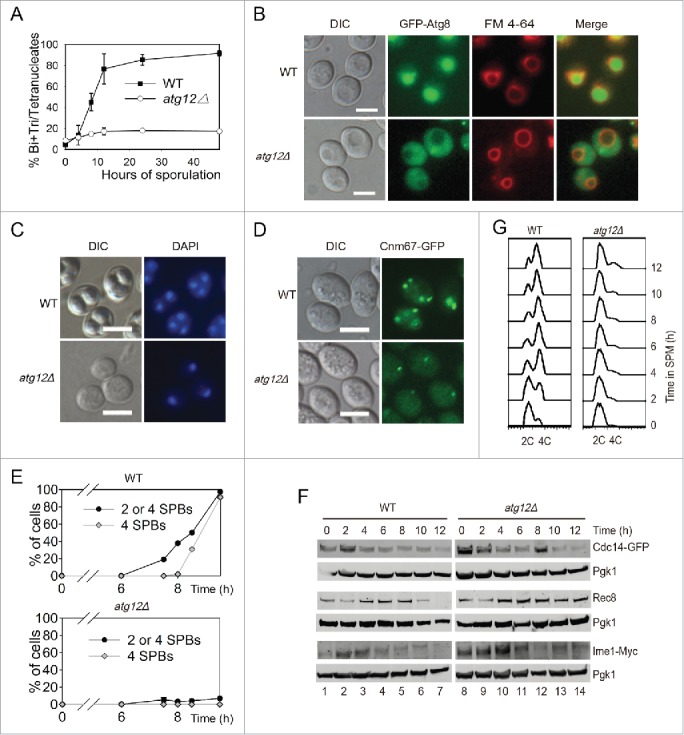
ATG12 deletion yeast cells arrested at the early stage of meiosis. (A-B) Sporulation defects in atg12Δ cells. (A) WT and atg12Δ strains were induced to sporulate at 30°C by transferring into SPM at the indicated times, and cells with 2–4 nuclei were counted as sporulated. (B) GFP-Atg8 localization after transfer into SPM. WT and atg12Δ cells expressing GFP-Atg8 was labeled by FM 4–64 then sporulated in SPM. After transfer into SPM for 4 h, cells were collected and immediately observed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars: 5 μm. DIC, differential interference contrast (C) DNA content of WT and atg12Δ strains during meiosis. Samples were collected 48 h after transfer to SPM. Scale bars: 10 µm. (D, E) SPBs failed to segregate in atg12Δ strains during meiosis. (D) SPBs were studied by fluorescence microscopy in WT and atg12Δ strains during meiosis. Scale bars: 5 µm. (E) Quantitative analysis of the SPBs during WT and atg12Δ cell meiosis. The error bar shows the SD of 3 independent experiments. (F) Effect of ATG12 knockout on Cdc14, Rec8 and Ime1 expression. Cdc14 was fused with GFP and detected with a GFP antibody. Ime1 was tagged with MYC for western blotting. Cells were transferred into SPM, and the same amount of samples was collected for protein extraction. Cdc14-GFP, Rec8 and Ime1-MYC were analyzed by western blotting. Lanes 1–14 represent samples at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 h in SPM for WT and atg12Δ cells, respectively. (G) Premeiotic DNA replication was retarded in the atg12Δ strain during meiosis. The DNA content of WT and atg12Δ cells was analyzed by flow cytometry at different sporulation time points.
