Figure 3.
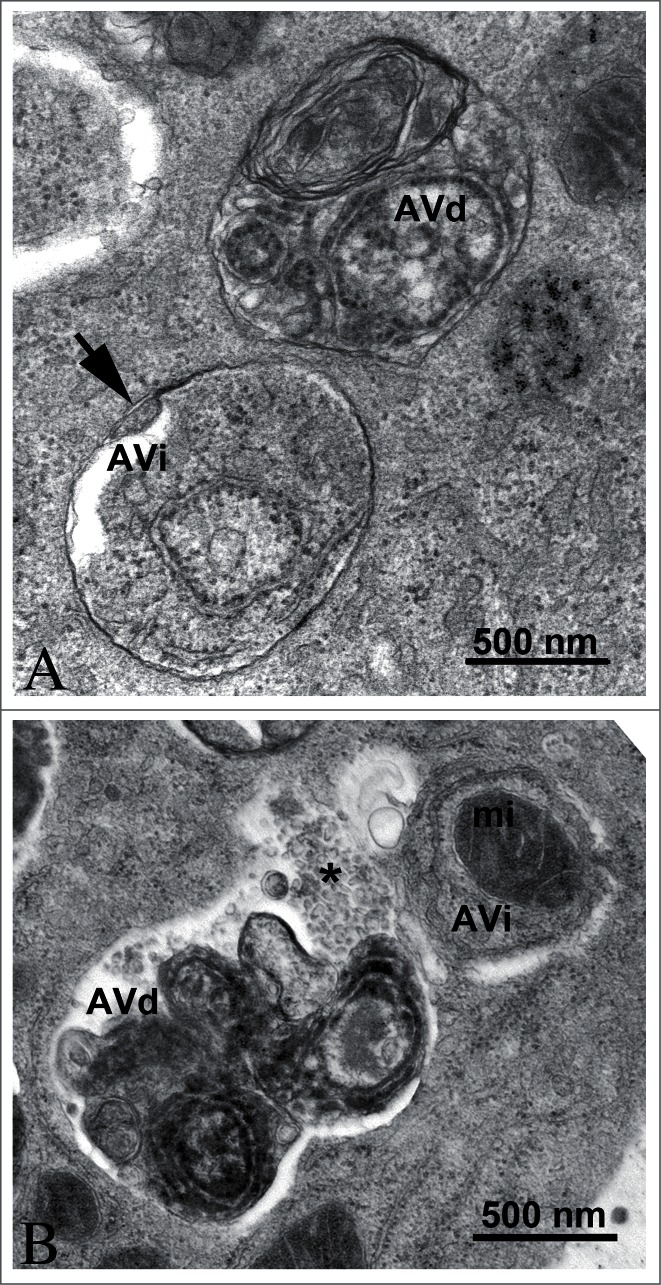
TEM images of autophagic vacuoles in isolated mouse hepatocytes. (A) One autophagosome or early initial autophagic vacuole (AVi) and one degradative autophagic vacuole (AVd) are shown. The AVi can be identified by its contents (morphologically intact cytoplasm, including ribosomes, and rough ER), and the limiting membrane that is partially visible as 2 bilayers separated by a narrow electron-lucent cleft, i.e., as a double membrane (arrow). The AVd can be identified by its contents, partially degraded, electron-dense rough ER. The vesicle next to the AVd is an endosomal/lysosomal structure containing 5-nm gold particles that were added to the culture medium to trace the endocytic pathway. (B) One AVi, containing rough ER and a mitochondrion, and one AVd, containing partially degraded rough ER, are shown. Note that the limiting membrane of the AVi is not clearly visible, possibly because it is tangentially sectioned. However, the electron-lucent cleft between the 2 limiting membranes is visible and helps in the identification of the AVi. The AVd contains a region filled by small internal vesicles (asterisk), indicating that the AVd has fused with a multivesicular endosome. mi, mitochondrion. Image provided by E.-L. Eskelinen.
