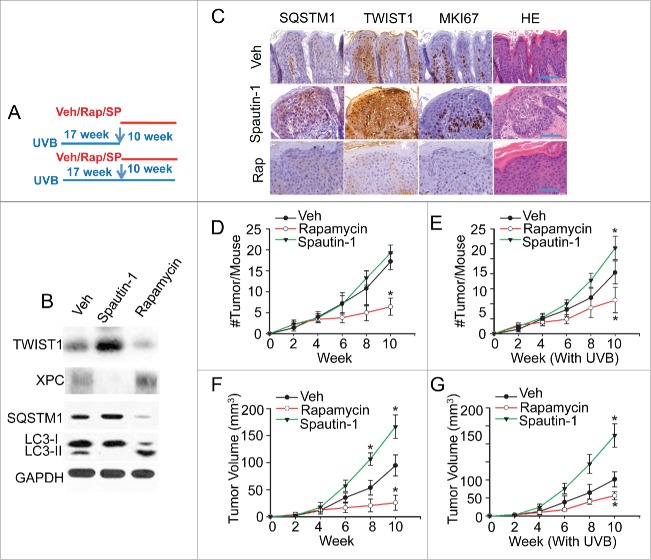
Figure 6.
Pharmacological modulators of autophagy regulate UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis. (A) A schematic diagram of the experimental design for B to G, in which mice were treated with UVB irradiation for 17 wk, 3 times per wk, and then with vehicle only or topical rapamycin (Rap, 10 nmol) or Spautin-1 (SP, 25 nmol) 3 h prior to each UVB or sham treatment 3 times a wk for another 10 wk. (B) Immunoblot analysis of LC3-I, LC3-II, SQSTM1, XPC, TWIST1 and GAPDH in mouse skin collected 12 h after the final treatment. (C) Representative histological and immunohistochemical analysis of SQSTM1, TWIST1, and MKI67 protein levels (brown) in UVB-irradiated mouse skin treated with Vehicle (Veh), rapamycin, or Spautin-1. Scale bar: 50 µm. (D, E) Number (#) of new tumors per mouse at different weeks following Rap or Spautin-1 treatment as in (A) (n=5), without (D) or with (E) continuing UVB irradiation. (F, G) Average volume (mm3) of established tumors formed at 17 wk post-UVB at different weeks following treatment as in (A), without (F) or with (G) continuing UVB irradiation. The results were mean±SD (n=5). *, P <0.05; **, P<0.01 compared with the Veh group in D to G). [Change label to Spautin-1.]