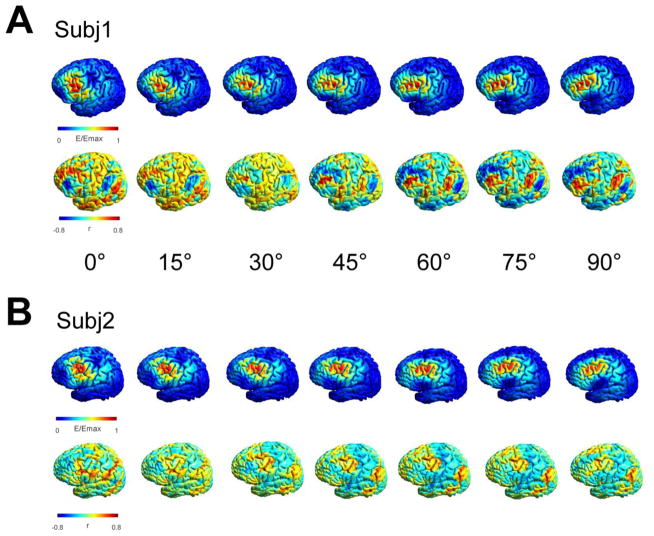
Figure 2.
Exemplary effect of coil orientation on the predicted functional network for two subjects. A) + B) Electric field distributions for seven different coil orientations (15 degree steps, 90 degree total difference) at the same location (lower panel). While the induced electric field distributions overlap to some extent in the central region common to all orientations, stronger differences occur in the periphery. The functional connectivity maps show a clearly different spatial pattern demonstrating the strong influence of a changing coil orientation on the underlying networks.