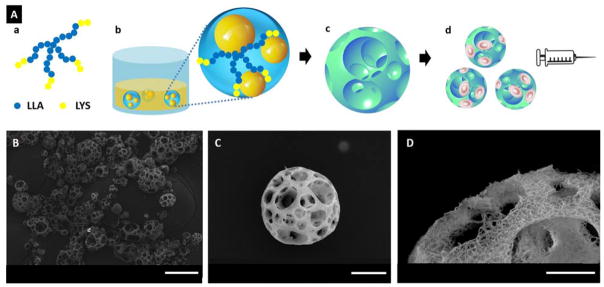
Figure 1.
(A) A schematic illustration of the fabrication of NF-SMS for stem cell delivery through injection. (a) SS-PLLA-b-PLYS; (b) Emulsions self-assembled from SS-PLLA-b-PLYS, with one polymer solution droplet containing multiple glycerol domains; (c) NF-SMS were obtained after phase separation and freeze-drying; (d) the porous structure of NF-SMS allow efficient cell loading and delivery through injection. (B–D) Characterization of nanofibrous spongy microspheres (NF-SMS). (B) SEM image of NF-SMS at low magnification. (C) SEM image of representative NF-SMS, showing the interconnected porous structure with a pore diameter around 10–20 μm. (D) High magnification image of (C) showing the NF architecture of the NF-SMS with an average fiber diameter of about 160 nm. Scale bars: (B) 100 μm, (C) 20 μm, (D) 10 μm.