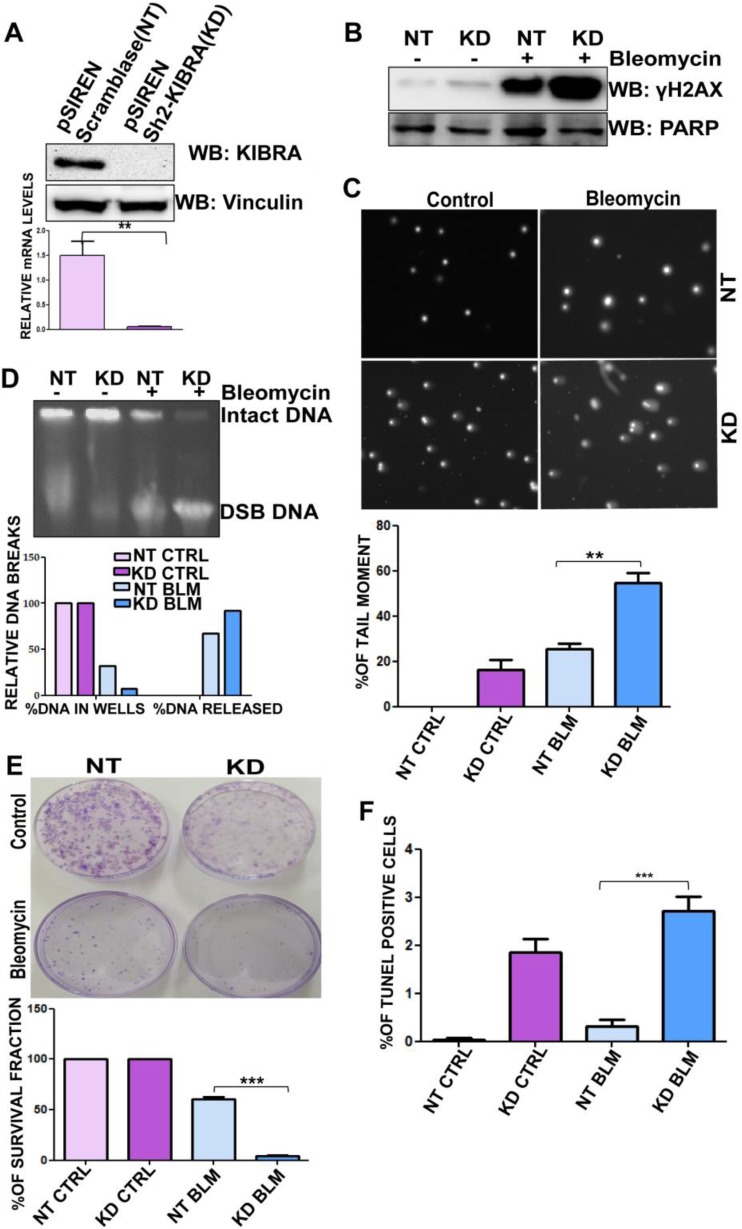
FIG 5.
Depleting KIBRA levels compromises the DNA repair functions of cancer cells. (A) Western blot and RT-PCR analyses showing KIBRA stable knockdown (KD) clones of the MDA-MB-231 cell line (t test). (B) MDA-MB-231 KIBRA-KD NT clones were treated or not treated with bleomycin for 2 h, proteins were separated using SDS-PAGE, and the blot was probed for γH2Ax (phosphoserine 139); anti-PARP was used as a loading control. (C) Neutral comet assay histogram showing the percentages of tail moment of comets assessed for 100 individual comets using CaspLab software. Percentages of tail moment were compared between MDA-MB-231 KIBRA-KD NT clones with or without bleomycin treatment (one-way ANOVA). (D) Percentages of DNA breaks with bleomycin treatment or without treatment of MDA-MB-231 KIBRA-KD NT clones. Undamaged DNA remained in wells; damaged DNA was released from wells. KIBRA KD clones had lower percentages of undamaged DNA than NT clones. (E) Percentages of survival of MDA-MB-231 KIBRA-KD NT clones over 18 days. Cells were seeded at 3,000 cells/plate after bleomycin treatment or without treatment for 2 h; the ability of KIBRA KD clones to form colonies was compromised upon treatment (one-way ANOVA). (F) Graph showing percentages of terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) populations of MDA-MB-231 KIBRA-KD NT clones with bleomycin treatment or without treatment. KIBRA KD clones showed higher percentages of breaks than NT clones (one-way ANOVA). **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.