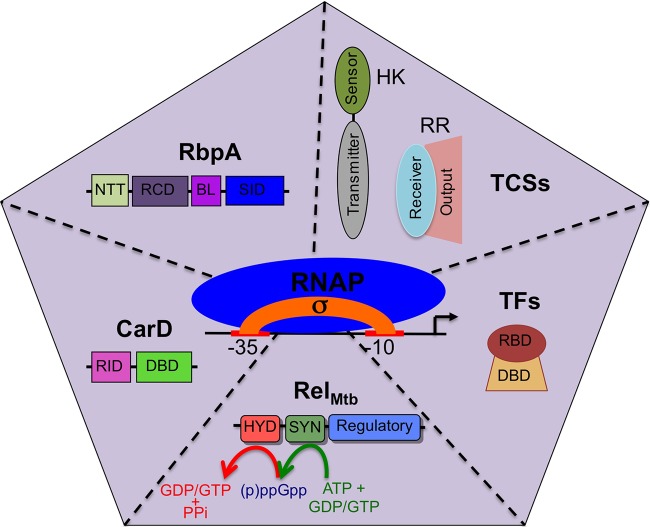
FIG 1.
Summary of the branches of transcriptional regulation that are discussed in this minireview. The illustration shows 6 types of factors (σ factors, CarD, RbpA, TCSs, TFs, and RelMtb) that modulate RNAP activity at promoters to mediate reprogramming of the expression profile in M. tuberculosis in response to different environments. A σ factor associates with the core RNAP to form the RNAP holoenzyme, which is then modified by the other factors shown in the sections of the pentagon. Domains of each protein are shown. For CarD, RID is the RNAP interaction domain and DBD is the DNA binding domain. For RbpA, NTT is the N-terminal tail, RCD is the RbpA core domain, BL is the basic linker, and SID is the sigma interaction domain. For RelMtb, HYD is the (p)ppGpp hydrolase domain and SYN is the (p)ppGpp synthetase domain. For TFs, RBD is the RNAP binding domain and DBD is the DNA binding domain. In the presence of a given stress, these factors coordinate their responses to effectively respond to host attacks.