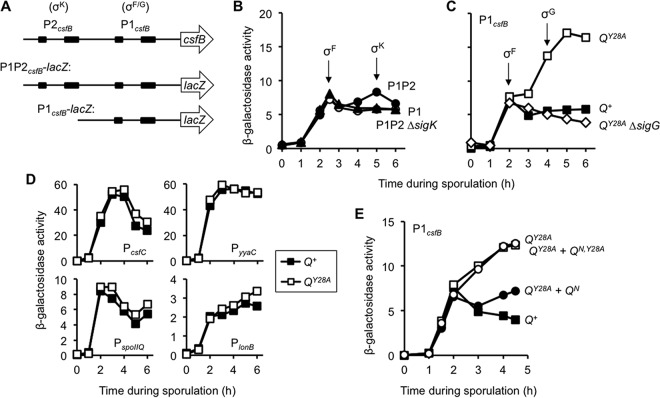
FIG 3.
Q Tyr-28 is required to prevent σG-dependent activation of the csfB promoter during sporulation. (A) Cartoon of the B. subtilis csfB upstream regulatory region. The −35 and −10 promoter elements recognized by σK (P2csfB) or σF and σG (P1csfB) are depicted as black boxes. The P1P2csfB-lacZ and P2csfB-lacZ reporter constructs are drawn to scale below. (B) P1csfB and P2csfB are activated by σF and σK, respectively, during sporulation. The accumulation of β-galactosidase from P1P2csfB-lacZ (P1P2; closed circles) and P1csfB-lacZ (P1; triangles) was measured during sporulation of otherwise wild-type cells. The activity of the P1P2csfB-lacZ reporter was also monitored in a strain lacking σK (P1P2 ΔsigK; open circles). Reporters were inserted at the amyE locus. P1P2, P1P2 ΔsigK, and P1 were carried by strains AHB1702, JDC5, and JDC138, respectively. (C) σG-dependent activation of PcsfB is unmasked in the QY28A mutant. Activation of the P1csfB-lacZ reporter was monitored during sporulation of strains harboring Q+ or QY28A (strains JDC142 and JDC143, respectively). P1csfB-lacZ activity was also measured in a QY28A strain lacking σG (QY28A ΔsigG; strain JDC150). In each of these strains, the native Q gene was deleted and either Q+ or QY28A was inserted at the sacA locus. Note that the y axis in panel C is the same as that in panel B. (D) The Q Tyr-28 substitution does not unmask σG activation of other σF-activated promoters. Four representative σF-dependent promoters (those of csfC, yyaC, spoIIQ, and lonB) were fused to lacZ and assayed for expression in both wild-type Q+ and QY28A mutant strains. Q+ and QY28A strains are strains EBM49 and EBM50, respectively, for PcsfC; strains EBM44 and EBM47, respectively, for PyyaC; strains EBM42 and EBM45, respectively, for PspoIIQ; and strains EBM43 and EMB46, respectively, for PlonB; in all of these strains, the lacZ reporter genes were inserted at amyE. Data are from representative, single experiments. (E) The 53-residue wild-type Q N terminus (QN) can restore proper P1csfB expression in the QY28A mutant. P1csfB-lacZ activity was monitored in strains harboring either Q+ or QY28A encoded at the lacA locus and was also monitored in QY28A strains that were complemented with either wild-type QN (QY28A + QN) or mutant QN,Y28A (QY28A + QN,Y28A) at the sacA locus (strains KF5, KF6, KF11, and KF12, respectively).