FIG 4.
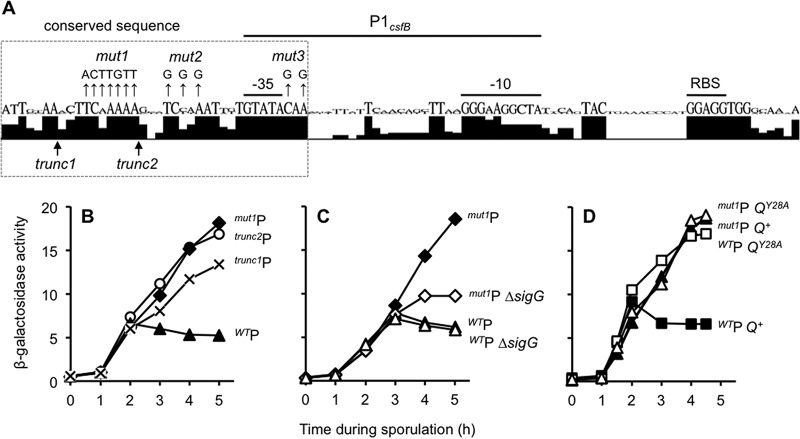
A regulatory element near P1csfB is necessary to prevent its activation by σG during sporulation. (A) A 37-nt sequence adjacent to the B. subtilis P1csfB −35 element is well conserved. The csfB regulatory sequences corresponding to the P1csfB-lacZ construct from B. subtilis, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. atrophaeus, B. licheniformis, and B. methylotrophicus were analyzed by the use of Geneious software to generate a sequence logo depiction of nucleotide conservation. Shown below the sequence logo are the 5′ boundaries of the trunc1P1csfB-lacZ and trunc2P1csfB-lacZ constructs. Nucleotides mutated in the mut1P1csfB-lacZ, mut2P1csfB-lacZ, and mut3P1csfB-lacZ constructs are indicated by mut1, mut2, and mut3, respectively. Note that the data obtained for the mut2P1csfB-lacZ and mut3P1csfB-lacZ constructs are presented in Fig. S4 in the supplemental material. RBS, ribosome binding site. (B) Activity of P1csfB variants during sporulation. β-Galactosidase production was monitored during the sporulation of strains harboring P1csfB-lacZ (WTP), trunc1P1csfB-lacZ, trunc2P1csfB-lacZ, and mut1P1csfB-lacZ reporter constructs integrated at amyE (strains KF76, KF159, AHB2088, and KF13, respectively). (C) The late activity of mut1P1csfB-lacZ is due to inappropriate activation by σG. β-Galactosidase production from the mut1P1csfB-lacZ reporter was assessed in a strain with native sigG (mut1P) or a strain from which sigG was deleted (mut1P ΔsigG). As a control, the wild-type P1csfB-lacZ reporter was also assessed in a strain with a native sigG (WTP) or a strain from which sigG was deleted (WTP ΔsigG). Reporter genes were inserted at the amyE locus in these strains (strains KF13, KF15, JDC138, and KF109, respectively). (D) Mutation of the csfB promoter element and substitution of Q Tyr-28 misregulate csfB expression to a similar extent and in a nonadditive manner. β-Galactosidase activity from the P1csfB-lacZ or mut1P1csfB-lacZ reporter constructs was measured in strains harboring Q+ or QY28A. The strains were P1csfB-lacZ Q+ (WTP Q+), P1csfB-lacZ QY28A (WTP QY28A), mut1P1csfB-lacZ Q+ (mut1P Q+), and mut1P1csfB-lacZ QY28A (mut1P QY28A) (strains KF1, KF2, KF3, and KF4, respectively). In each of these strains, the native Q gene was deleted and either Q+ or QY28A was inserted at the sacA locus; lacZ reporters were inserted at the amyE locus. Note that the y axes for panels C and D are the same as the y axis for panel B.